AMD3100 is a potent antagonist at CXCR4(R334X) , a hyperfunctional mutant chemokine receptor and cause of WHIM syndrome
- PMID: 21070597
- PMCID: PMC3071896
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01210.x
AMD3100 is a potent antagonist at CXCR4(R334X) , a hyperfunctional mutant chemokine receptor and cause of WHIM syndrome
Abstract
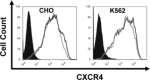
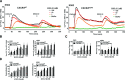
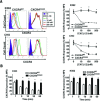
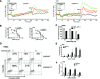
WHIM is an acronym for a rare immunodeficiency syndrome (OMIM #193670) caused by autosomal dominant mutations truncating the C-terminus of the chemokine receptor CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4). WHIM mutations may potentiate CXCR4 signalling, suggesting that the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved CXCR4 antagonist AnorMED3100 (AMD3100) (also known as Plerixafor) may be beneficial in WHIM syndrome. We have tested this at the preclinical level by comparing Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) and K562 cell lines matched for expression of recombinant wild-type CXCR4 (CXCR4(WT)) and the most common WHIM variant of CXCR4 (CXCR4(R334X)), as well as leucocytes from a WHIM patient with the CXCR4(R334X) mutation versus healthy controls. We found that CXCR4(R334X) mediated modestly increased signalling (~2-fold) in all functional assays tested, but strongly resisted ligand-dependent down-regulation. AMD3100 was equipotent and equieffective as an antagonist at CXCR4(R334X) and CXCR4(WT) . Together, our data provide further evidence that CXCR4(R334X) is a gain-of-function mutation, and support clinical evaluation of AMD3100 as mechanism-based treatment in patients with WHIM syndrome.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Gorlin RJ, Gelb B, Diaz GA, et al. WHIM syndrome, an autosomal dominant disorder: clinical, hematological, and molecular studies. Am J Med Genet. 2000;91:368–76. - PubMed
-
- Wetzler M, Talpaz M, Kleinerman ES, et al. A new familial immunodeficiency disorder characterized by severe neutropenia, a defective marrow release mechanism, and hypogammaglobulinemia. Am J Med. 1990;89:663–72. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez PA, Gorlin RJ, Lukens JN, et al. Mutations in the chemokine receptor gene CXCR4 are associated with WHIM syndrome, a combined immunodeficiency disease. Nat Genet. 2003;34:70–4. - PubMed
-
- Balabanian K, Lagane B, Pablos JL, et al. WHIM syndromes with different genetic anomalies are accounted for by impaired CXCR4 desensitization to CXCL12. Blood. 2005;105:2449–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

