Differential gene expression in nearly isogenic lines with QTL for partial resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley
- PMID: 21070652
- PMCID: PMC3018140
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-629
Differential gene expression in nearly isogenic lines with QTL for partial resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley
Abstract
Background: The barley-Puccinia hordei (barley leaf rust) pathosystem is a model for investigating partial disease resistance in crop plants and genetic mapping of phenotypic resistance has identified several quantitative trait loci (QTL) for partial resistance. Reciprocal QTL-specific near-isogenic lines (QTL-NILs) have been developed that combine two QTL, Rphq2 and Rphq3, the largest effects detected in a recombinant-inbred-line (RIL) population derived from a cross between the super-susceptible line L94 and partially-resistant line Vada. The molecular mechanism underpinning partial resistance in these QTL-NILs is unknown.
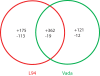
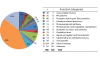
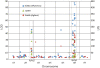
Results: An Agilent custom microarray consisting of 15,000 probes derived from barley consensus EST sequences was used to investigate genome-wide and QTL-specific differential expression of genes 18 hours post-inoculation (hpi) with Puccinia hordei. A total of 1,410 genes were identified as being significantly differentially expressed across the genome, of which 55 were accounted for by the genetic differences defined by QTL-NILs at Rphq2 and Rphq3. These genes were predominantly located at the QTL regions and are, therefore, positional candidates. One gene, encoding the transcriptional repressor Ethylene-Responsive Element Binding Factor 4 (HvERF4) was located outside the QTL at 71 cM on chromosome 1H, within a previously detected eQTL hotspot for defence response. The results indicate that Rphq2 or Rphq3 contains a trans-eQTL that modulates expression of HvERF4. We speculate that HvERF4 functions as an intermediate that conveys the response signal from a gene(s) contained within Rphq2 or Rphq3 to a host of down-stream defense responsive genes. Our results also reveal that barley lines with extreme or intermediate partial resistance phenotypes exhibit a profound similarity in their spectrum of Ph-responsive genes and that hormone-related signalling pathways are actively involved in response to Puccinia hordei.
Conclusions: Differential gene expression between QTL-NILs identifies genes predominantly located within the target region(s) providing both transcriptional and positional candidate genes for the QTL. Genetically mapping the differentially expressed genes relative to the QTL has the potential to discover trans-eQTL mediated regulatory relays initiated from genes within the QTL regions.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

