Rational design of modular circuits for gene transcription: A test of the bottom-up approach
- PMID: 21070658
- PMCID: PMC2993646
- DOI: 10.1186/1754-1611-4-14
Rational design of modular circuits for gene transcription: A test of the bottom-up approach
Abstract
Background: Most of synthetic circuits developed so far have been designed by an ad hoc approach, using a small number of components (i.e. LacI, TetR) and a trial and error strategy. We are at the point where an increasing number of modular, inter-changeable and well-characterized components is needed to expand the construction of synthetic devices and to allow a rational approach to the design.
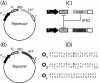
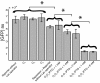
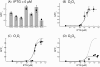
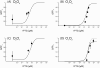
Results: We used interchangeable modular biological parts to create a set of novel synthetic devices for controlling gene transcription, and we developed a mathematical model of the modular circuits. Model parameters were identified by experimental measurements from a subset of modular combinations. The model revealed an unexpected feature of the lactose repressor system, i.e. a residual binding affinity for the operator site by induced lactose repressor molecules. Once this residual affinity was taken into account, the model properly reproduced the experimental data from the training set. The parameters identified in the training set allowed the prediction of the behavior of networks not included in the identification procedure.
Conclusions: This study provides new quantitative evidences that the use of independent and well-characterized biological parts and mathematical modeling, what is called a bottom-up approach to the construction of gene networks, can allow the design of new and different devices re-using the same modular parts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A synthetic post-transcriptional controller to explore the modular design of gene circuits.ACS Synth Biol. 2012 May 18;1(5):163-71. doi: 10.1021/sb200021s. Epub 2012 May 10. ACS Synth Biol. 2012. PMID: 23651154
-
Re-using biological devices: a model-aided analysis of interconnected transcriptional cascades designed from the bottom-up.J Biol Eng. 2017 Dec 14;11:50. doi: 10.1186/s13036-017-0090-3. eCollection 2017. J Biol Eng. 2017. PMID: 29255481 Free PMC article.
-
Parts & pools: a framework for modular design of synthetic gene circuits.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014 Oct 6;2:42. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2014.00042. eCollection 2014. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25340051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular construction of mammalian gene circuits using TALE transcriptional repressors.Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Mar;11(3):207-213. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1736. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Nat Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25643171 Free PMC article.
-
RTRACS: a modularized RNA-dependent RNA transcription system with high programmability.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Dec 20;44(12):1369-79. doi: 10.1021/ar200128b. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 22011083 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of an inducible promoter in different DNA copy number conditions.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Mar 28;13 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S4-S11. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22536957 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic biosensors for precise gene control and real-time monitoring of metabolites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 3;43(15):7648-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv616. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26152303 Free PMC article.
-
Reliable measurement of E. coli single cell fluorescence distribution using a standard microscope set-up.J Biol Eng. 2017 Feb 20;11:8. doi: 10.1186/s13036-017-0050-y. eCollection 2017. J Biol Eng. 2017. PMID: 28239411 Free PMC article.
-
Redesign of ultrasensitive and robust RecA gene circuit to sense DNA damage.Microb Biotechnol. 2021 Nov;14(6):2481-2496. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13767. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Microb Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33661573 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic Variability in Synthetic Biology Applications: Dealing with Noise in Microbial Gene Expression.Front Microbiol. 2016 Apr 8;7:479. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00479. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27092132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

