Differential expression of interferon-induced microRNAs in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection treated with pegylated interferon alpha
- PMID: 21070682
- PMCID: PMC2996368
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-311
Differential expression of interferon-induced microRNAs in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection treated with pegylated interferon alpha
Abstract
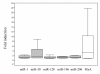
There have been reports of in-vitro interferon (IFN)-mediated antiviral activity against the hepatitis C virus (HCV) through microRNAs (miRNAs). The main aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of several miRNAs (miR-1, miR-30, miR-128, miR-196, miR-296) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy individuals after in vitro IFN-treatment and in PBMCs from patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) before and 12 hours after the first injection of pegylated IFN alpha. We demonstrated that expression of these miRNAs could be recorded in PBMCs collected from healthy individuals before and after in-vitro IFN alpha treatment. Our analysis revealed that the levels of expression of all miRNAs investigated in patients with CHC were different to those in healthy individuals. When levels of the miRNAs were measured 12 hours after the first IFN injection, increases in expression levels of IFN-induced miRNAs were observed in 25-50% of patients, depending on the type of miRNA examined. No correlations were observed between HCV viral load, alanine aminotransferase status and expression of miRNA. Together these findings suggest that: (i) IFN alpha in-vitro treatment of PBMCs leads to a transcriptional induction of all miRNAs investigated; (ii) miRNAs can be induced differentially by IFN treatment in patients with HCV. Given the importance of miRNAs in defending the host against virus infections, it is possible that IFN-induced miRNAs may represent an important determinant of the clinical outcome of IFN therapy in HCV infection.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

