Rescue of lethal hepatic failure by hepatized lymph nodes in mice
- PMID: 21070777
- PMCID: PMC3031768
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.11.006
Rescue of lethal hepatic failure by hepatized lymph nodes in mice
Abstract
Background & aims: Hepatocyte transplantation is a potential therapeutic approach for liver disease. However, most patients with chronic hepatic damage have cirrhosis and fibrosis, which limit the potential for cell-based therapy of the liver. The development of an ectopic liver as an additional site of hepatic function represents a new approach for patients with end-stage liver disease. We investigated the development and function of liver tissue in lymph nodes in mice with liver failure.
Methods: Hepatocytes were isolated from 8- to 12-week-old mice and transplanted by intraperitoneal injection into 8- to 12-week-old fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase mice (Fah(-/-)), a model of the human liver disease tyrosinemia type I. Survival was monitored and the locations and functions of the engrafted liver cells were determined.
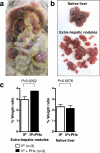
Results: Lymph nodes of Fah(-/-) mice were colonized by transplanted hepatocytes; Fah(+) hepatocytes were detected adjacent to the CD45(+) lymphoid cells of the lymphatic system. Ten weeks after transplantation, these mice had substantial improvements in serum levels of transaminases, bilirubin, and amino acids. Homeostatic expansion of donor hepatocytes in lymph nodes rescued the mice from lethal hepatic failure.
Conclusions: Functional ectopic liver tissue in lymph nodes rescues mice from lethal hepatic disease; lymph nodes therefore might be used as sites for hepatocyte transplantation.
Copyright © 2011 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures















Comment in
-
Transplantation: Functional ectopic liver tissue in the lymph nodes of mice with lethal liver disease.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Apr;8(4):182. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.25. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21595059 No abstract available.
References
-
- Perkins JD, Halldorson JB, Bakthavatsalam R, Fix OK, Carithers RL, Jr., Reyes JD. Should liver transplantation in patients with model for end-stage liver disease scores <or= 14 be avoided? A decision analysis approach. Liver Transpl. 2009;15:242–54. - PubMed
-
- Volk ML, Hernandez JC, Lok AS, Marrero JA. Modified Charlson comorbidity index for predicting survival after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2007;13:1515–20. - PubMed
-
- Lipshutz GS, Busuttil RW. Liver transplantation in those of advancing age: the case for transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2007;13:1355–7. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RA, Strom SC. Human hepatocyte transplantation: worldwide results. Transplantation. 2006;82:441–9. - PubMed
-
- Strom SC, Chowdhury JR, Fox IJ. Hepatocyte transplantation for the treatment of human disease. Semin Liver Dis. 1999;19:39–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

