Dietary n-6 PUFA deprivation downregulates arachidonate but upregulates docosahexaenoate metabolizing enzymes in rat brain
- PMID: 21070866
- PMCID: PMC3018563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.10.005
Dietary n-6 PUFA deprivation downregulates arachidonate but upregulates docosahexaenoate metabolizing enzymes in rat brain
Abstract
Background: Dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) deprivation increases expression of arachidonic acid (AA 20:4n-6)-selective cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) IVA and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in rat brain, while decreasing expression of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA 22:6n-3)-selective calcium-independent iPLA(2) VIA. Assuming that these enzyme changes represent brain homeostatic responses to deprivation, we hypothesized that dietary n-6 PUFA deprivation would produce changes in the opposite directions.
Methods: Brain expression of PUFA-metabolizing enzymes and their transcription factors was quantified in male rats fed an n-6 PUFA adequate or deficient diet for 15weeks post-weaning.
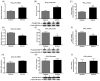
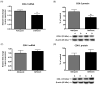
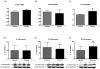
Results: The deficient compared with adequate diet increased brain mRNA, protein and activity of iPLA(2) VIA and 15-lipoxygenase (LOX), but decreased cPLA(2) IVA and COX-2 expression. The brain protein level of the iPLA(2) transcription factor SREBP-1 was elevated, while protein levels were decreased for AP-2α and NF-κB p65, cPLA(2) and COX-2 transcription factors, respectively.
Conclusions: With dietary n-6 PUFA deprivation, rat brain PUFA metabolizing enzymes and some of their transcription factors change in a way that would homeostatically dampen reductions in brain n-6 PUFA concentrations and metabolism, while n-3 PUFA metabolizing enzyme expression is increased. The changes correspond to reported in vitro enzyme selectivities for AA compared with DHA.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Farooqui AA, Yi Ong W, Lu XR, Halliwell B, Horrocks LA. Neurochemical consequences of kainate-induced toxicity in brain: involvement of arachidonic acid release and prevention of toxicity by phospholipase A(2) inhibitors. Brain research. 2001;38:61–78. - PubMed
-
- Innis SM. Essential fatty acids in infant nutrition: lessons and limitations from animal studies in relation to studies on infant fatty acid requirements. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2000;71:238S–244S. - PubMed
-
- Salem N, Jr, Litman B, Kim HY, Gawrisch K. Mechanisms of action of docosahexaenoic acid in the nervous system. Lipids. 2001;36:945–959. - PubMed
-
- Uauy R, Mena P, Rojas C. Essential fatty acids in early life: structural and functional role. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. 2000;59:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Clark JD, Lin LL, Kriz RW, Ramesha CS, Sultzman LA, Lin AY, Milona N, Knopf JL. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991;65:1043–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

