A reducible polycationic gene vector derived from thiolated low molecular weight branched polyethyleneimine linked by 2-iminothiolane
- PMID: 21071079
- PMCID: PMC2992579
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.08.079
A reducible polycationic gene vector derived from thiolated low molecular weight branched polyethyleneimine linked by 2-iminothiolane
Abstract
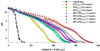
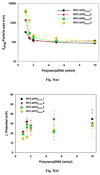
To improve transfection efficiency and reduce the cytotoxicity of polymeric gene vectors, reducible polycations (RPC) were synthesized from low molecular weight (MW) branched polyethyleneimine (bPEI) via thiolation and oxidation. RPC (RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa)) possessed MW of 5 kDa-80 kDa, and 50%-70% of the original proton buffering capacity of bPEI(0.8 kDa) was preserved in the final product. The cytotoxicity of RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa) was 8-19 times less than that of the gold standard of polymeric transfection reagents, bPEI(25 kDa). Although bPEI(0.8 kDa) exhibited poor gene condensing capacities (∼2 μm at a weight ratio (WR) of 40), RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa) effectively condensed plasmid DNA (pDNA) at a WR of 2. Moreover, RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa)/pDNA (WR ≥2) formed 100-200 nm-sized particles with positively charged surfaces (20-35 mV). In addition, the results of the present study indicated that thiol/polyanions triggered the release of pDNA from RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa)/pDNA via the fragmentation of RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa) and ion-exchange. With negligible polyplex-mediated cytotoxicity, the transfection efficiencies of RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa)/pDNA were approximately 1200-1500-fold greater than that of bPEI(0.8 kDa)/pDNA and were equivalent or superior (∼7-fold) to that of bPEI(25 kDa)/pDNA. Interestingly, the distribution of high MW RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa)/pDNA in the nucleus of the cell was higher than that of low MW RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa)/pDNA. Thus, the results of the present study suggest that RPC-bPEI(0.8 kDa) has the potential to effectively deliver genetic materials with lower levels of toxicity.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Kang HC, Lee ES, Na K, Bae YH. Stimuli-sensitive nanosystems: For drug and gene delivery. In: Torchilin VP, editor. Multifunctional Pharmaceutical Nanocarriers. New York: Springer; 2008. pp. 161–199.
-
- Kim YH, Park JH, Lee M, Kim YH, Park TG, Kim SW. Polyethylenimine with acid-labile linkages as a biodegradable gene carrier. J Control Release. 2005;103:209–219. - PubMed
-
- Manickam DS, Oupicky D. Polyplex gene delivery modulated by redox potential gradients. J Drug Target. 2006;14:519–526. - PubMed
-
- Meng F, Hennink WE, Zhong Z. Reduction-sensitive polymers and bioconjugates for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2009;30:2180–2198. - PubMed
-
- Oupicky D, Bisht HS, Manickam DS, Zhou QH. Stimulus-controlled delivery of drugs and genes. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2005;2:653–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

