IL-33 family members and asthma - bridging innate and adaptive immune responses
- PMID: 21071194
- PMCID: PMC3380518
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2010.10.006
IL-33 family members and asthma - bridging innate and adaptive immune responses
Abstract
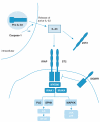
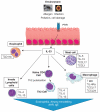
The discovery of IL-33 as the ligand for the orphan Th2 associated receptor ST2 has uncovered a whole range of different avenues for this pathway. Although the extracellular functions of ST2 as a marker for Th2 cell and mast cell activity were well defined, the complexities of IL-33 regulation, nuclear function and secretion are only just being realised. The well documented expression pattern of ST2 has identified a role for the IL-33/ST2 axis in the classical Th2 cell and mast cell driven pathogenesis of asthma and anaphylaxis. However, the induction of IL-33 expression by environmental or endogenous triggers now suggests a wider role for the pathway during infection, inflammation and tissue damage.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–490. - PubMed
-
- Smith DE. IL-33: a tissue derived cytokine pathway involved in allergic inflammation and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010;40:200–208. - PubMed
-
- Liew FY, Pitman NI, McInnes IB. Disease-associated functions of IL-33: the new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:103–110. - PubMed
-
- Tago K, Noda T, Hayakawa M, Iwahana H, Yanagisawa K, Yashiro T, Tominaga Si. Tissue distribution and subcellular localization of a variant form of the human ST2 gene product, ST2 V. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;285:1377–1383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

