The AddAB helicase-nuclease catalyses rapid and processive DNA unwinding using a single Superfamily 1A motor domain
- PMID: 21071401
- PMCID: PMC3064778
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1124
The AddAB helicase-nuclease catalyses rapid and processive DNA unwinding using a single Superfamily 1A motor domain
Abstract
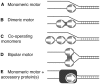
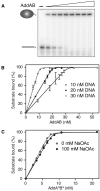
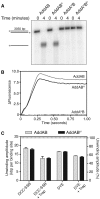
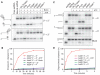
The oligomeric state of Superfamily I DNA helicases is the subject of considerable and ongoing debate. While models based on crystal structures imply that a single helicase core domain is sufficient for DNA unwinding activity, biochemical data from several related enzymes suggest that a higher order oligomeric species is required. In this work we characterize the helicase activity of the AddAB helicase-nuclease, which is involved in the repair of double-stranded DNA breaks in Bacillus subtilis. We show that the enzyme is functional as a heterodimer of the AddA and AddB subunits, that it is a rapid and processive DNA helicase, and that it catalyses DNA unwinding using one single-stranded DNA motor of 3' → 5' polarity located in the AddA subunit. The AddB subunit contains a second putative ATP-binding pocket, but this does not contribute to the observed helicase activity and may instead be involved in the recognition of recombination hotspot sequences.
Figures


References
-
- Gorbalenya AE, Koonin EV. Helicases - amino-acid-sequence comparisons and structure-function-relationships. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1993;3:419–429.
-
- Singleton MR, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB. Structure and mechanism of helicases and nucleic acid translocases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007;76:23–50. - PubMed
-
- Subramanya HS, Bird LE, Brannigan JA, Wigley DB. Crystal structure of a DExx box DNA helicase. Nature. 1996;384:379–383. - PubMed
-
- Kim JL, Morgenstern KA, Griffith JP, Dwyer MD, Thomson JA, Murcko MA, Lin C, Caron PR. Hepatitis C virus NS3 RNA helicase domain with a bound oligonucleotide: the crystal structure provides insights into the mode of unwinding. Structure. 1998;6:89–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

