Characterization of silent afferents in the pelvic and splanchnic innervations of the mouse colorectum
- PMID: 21071510
- PMCID: PMC3025511
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00406.2010
Characterization of silent afferents in the pelvic and splanchnic innervations of the mouse colorectum
Abstract
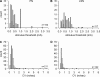
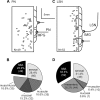
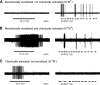
Hypersensitivity in inflammatory/irritable bowel syndrome is contributed to in part by changes in the receptive properties of colorectal afferent endings, likely including mechanically insensitive afferents (MIAs; silent afferents) that have the ability to acquire mechanosensitivity. The proportion and attributes of colorectal MIAs, however, have not previously been characterized. The distal ∼3 cm of colorectum with either pelvic (PN) or lumbar splanchnic (LSN) nerve attached was removed, opened longitudinally, pinned flat in a recording chamber, and perfused with oxygenated Krebs solution. Colorectal receptive endings were located by electrical stimulation and characterized as mechanosensitive or not by blunt probing, mucosal stroking, and circumferential stretch. MIA endings were tested for response to and acquisition of mechanosensitivity by localized exposure to an inflammatory soup (IS). Colorectal afferents were also tested with twin-pulse and repetitive electrical stimulation paradigms. PN MIAs represented 23% of 211 afferents studied, 71% (30/42) of which acquired mechanosensitivity after application of IS to their receptive ending. LSN MIAs represented 33% of 156 afferents studied, only 23% (11/48) of which acquired mechanosensitivity after IS exposure. Mechanosensitive PN endings uniformly exhibited significant twin-pulse slowing whereas LSN endings showed no significant twin-pulse difference. PN MIAs displayed significantly greater activity-dependent slowing than LSN MIAs. In conclusion, significant proportions of MIAs are present in the colorectal innervation; significantly more in the PN than LSN acquire mechanosensitivity in an inflammatory environment. This knowledge contributes to our understanding of the possible roles of MIAs in colon-related disorders like inflammatory/irritable bowel syndrome.
Figures




References
-
- Anand U, Otto WR, Facer P, Zebda N, Selmer I, Gunthorpe MJ, Chessell IP, Sinisi M, Birch R, Anand P. TRPA1 receptor localisation in the human peripheral nervous system and functional studies in cultured human and rat sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett 438: 221–227, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Berthoud HR, Blackshaw LA, Brookes SJ, Grundy D. Neuroanatomy of extrinsic afferents supplying the gastrointestinal tract. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16, Suppl 1: 28–33, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Brierley SM, Hughes PA, Page AJ, Kwan KY, Martin CM, O'Donnell TA, Cooper NJ, Harrington AM, Adam B, Liebregts T, Holtmann G, Corey DP, Rychkov GY, Blackshaw LA. The ion channel TRPA1 is required for normal mechanosensation and is modulated by algesic stimuli. Gastroenterology 137: 2084–2095, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

