Protein kinase C upregulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and leukocyte-endothelium interactions in hyperglycemia via activation of endothelial expressed calpain
- PMID: 21071702
- PMCID: PMC3086836
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.217901
Protein kinase C upregulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and leukocyte-endothelium interactions in hyperglycemia via activation of endothelial expressed calpain
Abstract
Objective: We tested the hypothesis of a role for the calcium-dependent protease calpain in the endothelial dysfunction induced by hyperglycemic activation of protein kinase C (PKC).
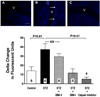
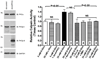
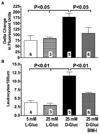
Methods and results: Chronic hyperglycemia with insulin deficiency (type 1 diabetes) was induced in rats by streptozotocin. Total PKC and calpain activities, along with activity and expression level of the 2 endothelial-expressed calpains isoforms, μ- and m-calpain, were measured in vascular tissue homogenates by enzymatic assays and Western blot analysis, respectively. Intravital microscopy was used to measure and correlate leukocyte-endothelium interactions with calpain activity in the microcirculation. Expression levels and endothelial localization of the inflammatory adhesion molecule intercellular adhesion molecule-1 were studied by Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence, respectively. The mechanistic role of hyperglycemia alone in the process of PKC-induced calpain activation and actions was also investigated. We found that in the type 1 diabetic vasculature, PKC selectively upregulates the activity of the μ-calpain isoform. Mechanistic studies confirmed a role for hyperglycemia and PKCβ in this process. The functional implications of PKC-induced calpain activation were upregulation of endothelial expressed intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and leukocyte-endothelium interactions.
Conclusions: Our results uncover the role of μ-calpain in the endothelial dysfunction of PKC. Calpain may represent a novel molecular target for the treatment of PKC-associated diabetic vascular disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A novel role for calpain in the endothelial dysfunction induced by activation of angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling.Circ Res. 2011 Apr 29;108(9):1102-11. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.229393. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21415394 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of hyperglycemic and hyperosmotic induced vascular dysfunction by in vivo inhibition of protein kinase C and p38 MAP kinase pathway in the rat mesenteric microcirculation.Eur J Clin Invest. 2000 Jul;30(7):586-93. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.2000.00680.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10886298
-
Hyperglycemia is a major determinant of albumin permeability in diabetic microcirculation: the role of mu-calpain.Diabetes. 2007 Jul;56(7):1842-9. doi: 10.2337/db06-1198. Epub 2007 Apr 19. Diabetes. 2007. PMID: 17446533
-
The role of protein kinase C activation and the vascular complications of diabetes.Pharmacol Res. 2007 Jun;55(6):498-510. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2007.04.016. Epub 2007 May 5. Pharmacol Res. 2007. PMID: 17574431 Review.
-
Protein kinase C beta inhibition: A novel therapeutic strategy for diabetic microangiopathy.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2006 Dec;3(3):172-8. doi: 10.3132/dvdr.2006.026. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2006. PMID: 17160912 Review.
Cited by
-
μ-Calpain as a Novel Target for Impairment of Nitric Oxide-Mediated Vascular Relaxation in Diabetes: A Mini Review.J Mol Genet Med. 2015 May;9(2):167. doi: 10.4172/1747-0862.1000167. J Mol Genet Med. 2015. PMID: 26120352 Free PMC article.
-
Selective deletion of endothelial cell calpain in mice reduces diabetic cardiomyopathy by improving angiogenesis.Diabetologia. 2019 May;62(5):860-872. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4828-y. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 30778623 Free PMC article.
-
Reconsidering the role of glycaemic control in cardiovascular disease risk in type 2 diabetes: A 21st century assessment.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022 Dec;24(12):2297-2308. doi: 10.1111/dom.14830. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022. PMID: 35929480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leukocyte Calpain Deficiency Reduces Angiotensin II-Induced Inflammation and Atherosclerosis But Not Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 May;36(5):835-45. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307285. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26966280 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain inhibition attenuates angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysms and atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;59(1):66-76. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e318235d5ea. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21964156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rask-Madsen C, King GL. Mechanisms of disease: Endothelial dysfunction in insulin resistance and diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007;3:46–56. - PubMed
-
- Munzel T, Sinning C, Post F, Warnholtz A, Schulz E. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and prognostic implications of endothelial dysfunction. Ann Med. 2008;40:180–196. - PubMed
-
- Marfella R, Esposito K, Giunta R, Coppola G, De Angelis L, Farzati B, Paolisso G, Giugliano D. Circulating adhesion molecules in humans: Role of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. Circulation. 2000;101:2247–2251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

