Protein kinase C upregulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and leukocyte-endothelium interactions in hyperglycemia via activation of endothelial expressed calpain
- PMID: 21071702
- PMCID: PMC3086836
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.217901
Protein kinase C upregulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and leukocyte-endothelium interactions in hyperglycemia via activation of endothelial expressed calpain
Abstract
Objective: We tested the hypothesis of a role for the calcium-dependent protease calpain in the endothelial dysfunction induced by hyperglycemic activation of protein kinase C (PKC).
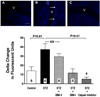
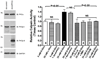
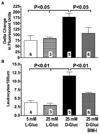
Methods and results: Chronic hyperglycemia with insulin deficiency (type 1 diabetes) was induced in rats by streptozotocin. Total PKC and calpain activities, along with activity and expression level of the 2 endothelial-expressed calpains isoforms, μ- and m-calpain, were measured in vascular tissue homogenates by enzymatic assays and Western blot analysis, respectively. Intravital microscopy was used to measure and correlate leukocyte-endothelium interactions with calpain activity in the microcirculation. Expression levels and endothelial localization of the inflammatory adhesion molecule intercellular adhesion molecule-1 were studied by Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence, respectively. The mechanistic role of hyperglycemia alone in the process of PKC-induced calpain activation and actions was also investigated. We found that in the type 1 diabetic vasculature, PKC selectively upregulates the activity of the μ-calpain isoform. Mechanistic studies confirmed a role for hyperglycemia and PKCβ in this process. The functional implications of PKC-induced calpain activation were upregulation of endothelial expressed intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and leukocyte-endothelium interactions.
Conclusions: Our results uncover the role of μ-calpain in the endothelial dysfunction of PKC. Calpain may represent a novel molecular target for the treatment of PKC-associated diabetic vascular disease.
Figures



References
-
- Rask-Madsen C, King GL. Mechanisms of disease: Endothelial dysfunction in insulin resistance and diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007;3:46–56. - PubMed
-
- Munzel T, Sinning C, Post F, Warnholtz A, Schulz E. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and prognostic implications of endothelial dysfunction. Ann Med. 2008;40:180–196. - PubMed
-
- Marfella R, Esposito K, Giunta R, Coppola G, De Angelis L, Farzati B, Paolisso G, Giugliano D. Circulating adhesion molecules in humans: Role of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. Circulation. 2000;101:2247–2251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

