Novel lipid mediators promote resolution of acute inflammation: impact of aspirin and statins
- PMID: 21071715
- PMCID: PMC3027152
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223883
Novel lipid mediators promote resolution of acute inflammation: impact of aspirin and statins
Abstract
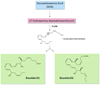
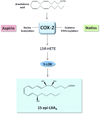
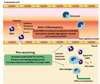
The resolution of acute inflammation is a process that allows for inflamed tissues to return to homeostasis. Resolution was held to be a passive process, a concept now overturned with new evidence demonstrating that resolution is actively orchestrated by distinct cellular events and endogenous chemical mediators. Among these, lipid mediators, such as the lipoxins, resolvins, protectins, and newly identified maresins, have emerged as a novel genus of potent and stereoselective players that counter-regulate excessive acute inflammation and stimulate molecular and cellular events that define resolution. Given that uncontrolled, chronic inflammation is associated with many cardiovascular pathologies, an appreciation of the endogenous pathways and mediators that control timely resolution can open new terrain for therapeutic approaches targeted at stimulating resolution of local inflammation, as well as correcting the impact of chronic inflammation in cardiovascular disorders. Here, we overview and update the biosynthesis and actions of proresolving lipid mediators, highlighting their diverse protective roles relevant to vascular systems and their relation to aspirin and statin therapies.
Figures

References
-
- Serhan CN, Savill J. Resolution of inflammation: The beginning programs the end. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1191–1197. - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E. Biomarkers in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2148–2159. - PubMed
-
- Ellis CR, Di Salvo T. Myocarditis: Basic and clinical aspects. Cardiol Rev. 2007;15:170–177. - PubMed
-
- Rocha VZ, Libby P. Obesity, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009;6:399–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

