C/EBPδ gene targets in human keratinocytes
- PMID: 21072181
- PMCID: PMC2970548
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013789
C/EBPδ gene targets in human keratinocytes
Abstract
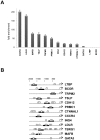
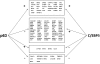
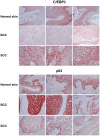
C/EBPs are a family of B-Zip transcription factors--TFs--involved in the regulation of differentiation in several tissues. The two most studied members--C/EBPα and C/EBPβ--play important roles in skin homeostasis and their ablation reveals cells with stem cells signatures. Much less is known about C/EBPδ which is highly expressed in the granular layer of interfollicular epidermis and is a direct target of p63, the master regular of multilayered epithelia. We identified C/EBPδ target genes in human primary keratinocytes by ChIP on chip and profiling of cells functionally inactivated with siRNA. Categorization suggests a role in differentiation and control of cell-cycle, particularly of G2/M genes. Among positively controlled targets are numerous genes involved in barrier function. Functional inactivation of C/EBPδ as well as overexpressions of two TF targets--MafB and SOX2--affect expression of markers of keratinocyte differentiation. We performed IHC on skin tumor tissue arrays: expression of C/EBPδ is lost in Basal Cell Carcinomas, but a majority of Squamous Cell Carcinomas showed elevated levels of the protein. Our data indicate that C/EBPδ plays a role in late stages of keratinocyte differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



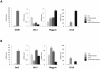

Similar articles
-
Reciprocal regulation of p63 by C/EBP delta in human keratinocytes.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Sep 28;8:85. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-85. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17903252 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins (C/EBP) is associated with squamous differentiation in epidermis and isolated primary keratinocytes and is altered in skin neoplasms.J Invest Dermatol. 1998 Jun;110(6):939-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00199.x. J Invest Dermatol. 1998. PMID: 9620302
-
C/EBP transcription factors in human squamous cell carcinoma: selective changes in expression of isoforms correlate with the neoplastic state.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 17;9(11):e112073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112073. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25402211 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor MafB Coordinates Epidermal Keratinocyte Differentiation.J Invest Dermatol. 2016 Sep;136(9):1848-1857. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.05.088. Epub 2016 May 18. J Invest Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27208706 Review.
-
C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ transcription factors: Basic biology and roles in the CNS.Prog Neurobiol. 2015 Sep;132:1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Prog Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26143335 Review.
Cited by
-
The many faces of C/EBPδ and their relevance for inflammation and cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Sep 20;9(9):917-33. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7224. eCollection 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24155666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAFB as a novel regulator of human adipose tissue inflammation.Diabetologia. 2015 Sep;58(9):2115-23. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3673-x. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 26115698
-
A LncRNA-MAF:MAFB transcription factor network regulates epidermal differentiation.Dev Cell. 2015 Mar 23;32(6):693-706. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.01.028. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 25805135 Free PMC article.
-
Basic biology and roles of CEBPD in cardiovascular disease.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Mar 14;11(1):102. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02357-4. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40087290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of cleft lip and cleft palate.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2013 Nov;163C(4):246-58. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31381. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2013. PMID: 24124047 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang ND, Finegold MJ, Bradley A, Ou CN, Abdelsayed SV, et al. Impaired energy homeostasis in C/EBPalpha knockout mice. Science. 1995;269:1108–12. - PubMed

