Targeting diphtheria toxin and TNF alpha expression in ovarian tumors using the H19 regulatory sequences
- PMID: 21072261
- PMCID: PMC2971537
Targeting diphtheria toxin and TNF alpha expression in ovarian tumors using the H19 regulatory sequences
Abstract
Background: There are currently no effective therapies for the treatment of ovarian cancer ascites fluid (OCAF). H19 is an RNA oncofetal gene that is present at high levels in human cancer tissues (ovarian cancer and OCAF among them), while existing at a nearly undetectable level in the surrounding normal tissue. There is evidence for a synergistic effect in cell cytotoxicity mediated by TNFα and diphtheria toxin in sensitive and resistant human ovarian tumor cell line. Thus, we tested the cytotoxic effect of TNF-α cytokine, together with the diphtheria toxin, in the therapy of ovarian cancer.
Methods: The therapeutic potential of toxin vectors carrying the DT-A gene alone (pH19-DTA), or in combination with the TNF-α gene (pH19-TNF-DTA), driven by H19 regulatory sequences were tested in ovarian carcinoma cell lines and in a heterotopic ovarian cancer model.
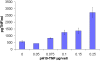
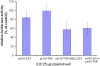
Results: The toxin vectors showed a high killing capacity when transfected into different ovarian cancer cell lines. In addition, intratumoral injection of the toxin vector into ectopically developed tumors caused 40% inhibition of tumor growth. The killing effect after injection of pH19-TNF-DTA plasmid into ectopically developed tumors was significantly higher than that showed by the pH19-DTA plasmid alone, particularly in diphtheria toxin and TNF resistant tumors.
Conclusions: These observations may be the first step towards a major breakthrough in the treatment of human ovarian cancer. It should enable us to identify likely non-responders in advance, and to treat patients who are resistant to all known therapies, thereby avoiding treatment failure coupled with unnecessary suffering and cost.
Keywords: DT-A; H19; IRES; TNF; ascites; ovarian cancer.
Figures




References
-
- Cannistra SA. Cancer of the ovary. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2519–252. - PubMed
-
- Louis MH, Dutoit S, Denoux Y, Erbacher P, De-slandes E, Behr JP, P Gauduchon1, L Poulain. Intraperitoneal linear polyethylenimine (L-PEI)-mediated gene delivery to ovarian carcinoma nodes in mice. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006;13:367–74. - PubMed
-
- Jandu N, Richardson M, Singh G, Hirte H, Hatton MW. Human ovarian cancer ascites fluid contains a mixture of incompletely degraded soluble products of fibrin that collectively possess an antiangiogenic property. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006;16:1536–44. - PubMed
-
- Gu J, Fang B. Telomerase promoter-driven cancer gene therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2:S64–S70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
