Biochemistry, evolution and physiological function of the Rnf complex, a novel ion-motive electron transport complex in prokaryotes
- PMID: 21072677
- PMCID: PMC11115008
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0555-8
Biochemistry, evolution and physiological function of the Rnf complex, a novel ion-motive electron transport complex in prokaryotes
Abstract
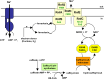
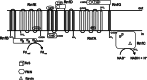
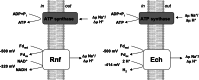
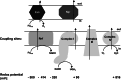
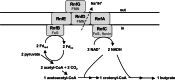
Microbes have a fascinating repertoire of bioenergetic enzymes and a huge variety of electron transport chains to cope with very different environmental conditions, such as different oxygen concentrations, different electron acceptors, pH and salinity. However, all these electron transport chains cover the redox span from NADH + H(+) as the most negative donor to oxygen/H(2)O as the most positive acceptor or increments thereof. The redox range more negative than -320 mV has been largely ignored. Here, we have summarized the recent data that unraveled a novel ion-motive electron transport chain, the Rnf complex, that energetically couples the cellular ferredoxin to the pyridine nucleotide pool. The energetics of the complex and its biochemistry, as well as its evolution and cellular function in different microbes, is discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Drake HL, Daniel S, Küsel K, Matthies C, Kuhner C, Braus-Strohmeyer S. Acetogenic bacteria: what are the in situ consequences of their diverse metabolic diversities? Biofactors. 1997;1:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Müller V, Imkamp F, Rauwolf A, Küsel K, Drake HL. Molecular and cellular biology of acetogenic bacteria. In: Nakano MM, Zuber P, editors. Strict and facultative anaerobes. Medical and environmental aspects. Norfolk: Horizon Biosciences; 2004. pp. 251–281.
-
- Diekert G, Wohlfarth G. Metabolism of homoacetogens. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Int J Gen M. 1994;66:209–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

