Transformation system for Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei) that favors homologous integration and employs reusable bidirectionally selectable markers
- PMID: 21075888
- PMCID: PMC3019734
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02100-10
Transformation system for Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei) that favors homologous integration and employs reusable bidirectionally selectable markers
Abstract
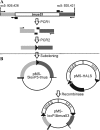
Hypocrea jecorina is an industrially important filamentous fungus due to its effective production of hydrolytic enzymes. It has received increasing interest because of its ability to convert lignocellulosic biomass to monomeric sugars, which can be converted into biofuels or platform chemicals. Genetic engineering of strains is a highly important means of meeting the requirements of tailor-made applications. Therefore, we report the development of a transformation system that allows highly efficient gene targeting by using a tmus53 (human LIG4 homolog) deletion strain. Moreover, it permits the unlimited reuse of the same marker by employing a Cre/loxP-based excision system. Both marker insertion and marker excision can be positively selected for by combining resistance to hygromycin B and loss of sensitivity to fluoroacetamide. Finally, the marker pyr4, also positively selectable for insertion and loss, can be used to remove the cre gene.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel carbon source-dependent genetic transformation system for the versatile cell factory Hypocrea jecorina (anamorph Trichoderma reesei).FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010 Feb;303(1):26-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01851.x. Epub 2009 Nov 13. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20002748
-
Gene targeting in a nonhomologous end joining deficient Hypocrea jecorina.J Biotechnol. 2009 Jan 15;139(2):146-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.10.007. Epub 2008 Nov 5. J Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19027803
-
Sequential gene deletions in Hypocrea jecorina using a single blaster cassette.Curr Genet. 2005 Sep;48(3):204-11. doi: 10.1007/s00294-005-0011-8. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Curr Genet. 2005. PMID: 16091959 Review.
-
Simple and efficient recycling of fungal selectable marker genes with the Cre-loxP recombination system via anastomosis.Fungal Genet Biol. 2013 Dec;61:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2013.08.013. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Fungal Genet Biol. 2013. PMID: 24007936 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous protein expression in Hypocrea jecorina: a historical perspective and new developments.Biotechnol Adv. 2015 Jan-Feb;33(1):142-154. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.11.009. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Biotechnol Adv. 2015. PMID: 25479282 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Transformation of Trichoderma spp.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2290:171-185. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1323-8_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34009590
-
Development of a low-cost cellulase production process using Trichoderma reesei for Brazilian biorefineries.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 Feb 2;10:30. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0717-0. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 28184245 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of an antiviral drug precursor from chitin using a saprophyte as a whole-cell catalyst.Microb Cell Fact. 2011 Dec 5;10:102. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-10-102. Microb Cell Fact. 2011. PMID: 22141613 Free PMC article.
-
The Kinase USK1 Regulates Cellulase Gene Expression and Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis in Trichoderma reesei.Front Microbiol. 2020 May 20;11:974. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00974. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32508786 Free PMC article.
-
The Cerato-Platanin protein Epl-1 from Trichoderma harzianum is involved in mycoparasitism, plant resistance induction and self cell wall protection.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 9;5:17998. doi: 10.1038/srep17998. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26647876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin, S., M. Ziese, and N. Sternberg. 1981. A novel role for site-specific recombination in maintenance of bacterial replicons. Cell 25:729-736. - PubMed
-
- Buchert, J., T. Oksanen, J. Pere, M. Siika-aho, A. Suurnäkki, and L. Viikari. 1998. Applications of Trichoderma reesei enzymes in the pulp and paper industry, p. 343-357. In G. E. Harman and C. P. Kubicek (ed.), Trichoderma and Gliocladium, vol. 2. Taylor & Francis Ltd., London, United Kingdom.
-
- Christianson, T. W., R. S. Sikorski, M. Dante, J. H. Shero, and P. Hieter. 1992. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene 110:119-122. - PubMed
-
- Colot, H. V., G. Park, G. E. Turner, C. Ringelberg, C. M. Crew, L. Litvinkova, R. L. Weiss, K. A. Borkovich, and J. C. Dunlap. 2006. A high-throughput gene knockout procedure for Neurospora reveals functions for multiple transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103:10352-10357. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dennison, P. M., M. Ramsdale, C. L. Manson, and A. J. Brown. 2005. Gene disruption in Candida albicans using a synthetic, codon-optimised Cre-loxP system. Fungal Genet. Biol. 42:737-748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

