Differential protein expression in Streptococcus uberis under planktonic and biofilm growth conditions
- PMID: 21075893
- PMCID: PMC3019713
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01099-10
Differential protein expression in Streptococcus uberis under planktonic and biofilm growth conditions
Abstract
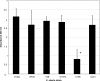
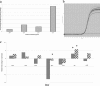
The bovine pathogen Streptococcus uberis was assessed for biofilm growth. The transition from planktonic to biofilm growth in strain 0140J correlated with an upregulation of several gene products that have been shown to be important for pathogenesis, including a glutamine ABC transporter (SUB1152) and a lactoferrin binding protein (gene lbp; protein SUB0145).
Figures
References
-
- Reference deleted.
-
- Blondeau, F., B. Ritter, P. D. Allaire, S. Wasiak, M. Girard, N. K. Hussain, A. Angers, V. Legendre-Guillemin, L. Roy, D. Boismenu, R. E. Kearney, A. W. Bell, J. J. Bergeron, and P. S. McPherson. 2004. Tandem MS analysis of brain clathrin-coated vesicles reveals their critical involvement in synaptic vesicle recycling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101:3833-3838. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Christensen, G. D., W. A. Simpson, J. J. Younger, L. M. Baddour, F. F. Barrett, D. M. Melton, and E. H. Beachey. 1985. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J. Clin. Microbiol. 22:996-1006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reference deleted.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

