Increased propensity for cell death in diabetic human heart is mediated by mitochondrial-dependent pathways
- PMID: 21076025
- PMCID: PMC3023249
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00932.2010
Increased propensity for cell death in diabetic human heart is mediated by mitochondrial-dependent pathways
Abstract
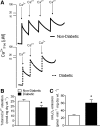
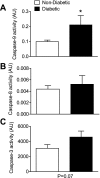
Progressive energy deficiency and loss of cardiomyocyte numbers are two prominent factors that lead to heart failure in experimental models. Signals that mediate cardiomyocyte cell death have been suggested to come from both extrinsic (e.g., cytokines) and intrinsic (e.g., mitochondria) sources, but the evidence supporting these mechanisms remains unclear, and virtually nonexistent in humans. In this study, we investigated the sensitivity of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) to calcium (Ca(2+)) using permeabilized myofibers of right atrium obtained from diabetic (n = 9) and nondiabetic (n = 12) patients with coronary artery disease undergoing nonemergent coronary revascularization surgery. Under conditions that mimic the energetic state of the heart in vivo (pyruvate, glutamate, malate, and 100 μM ADP), cardiac mitochondria from diabetic patients show an increased sensitivity to Ca(2+)-induced mPTP opening compared with nondiabetic patients. This increased mPTP Ca(2+) sensitivity in diabetic heart mitochondria is accompanied by a substantially greater rate of mitochondrial H(2)O(2) emission under identical conditions, despite no differences in respiratory capacity under these conditions or mitochondrial enzyme content. Activity of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway mediator caspase-9 was greater in diabetic atrial tissue, whereas activity of the extrinsic pathway mediator caspase-8 was unchanged between groups. Furthermore, caspase-3 activity was not significantly increased in diabetic atrial tissue. These data collectively suggest that the myocardium in diabetic patients has a greater overall propensity for mitochondrial-dependent cell death, possibly as a result of metabolic stress-imposed changes that have occurred within the mitochondria, rendering them more susceptible to insults such as Ca(2+) overload. In addition, they lend further support to the notion that mitochondria represent a viable target for future therapies directed at ameliorating heart failure and other comorbidities that come with diabetes.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson EJ, Lustig ME, Boyle KE, Woodlief TL, Kane DA, Lin CT, Price JW, 3rd, Kang L, Rabinovitch PS, Szeto HH, Houmard JA, Cortright RN, Wasserman DH, Neufer PD. Mitochondrial H2O2 emission and cellular redox state link excess fat intake to insulin resistance in both rodents and humans. J Clin Invest 119: 573–581, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson EJ, Yamazaki H, Neufer PD. Induction of endogenous uncoupling protein 3 suppresses mitochondrial oxidant emission during fatty acid-supported respiration. J Biol Chem 282: 31257–31266, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Ares-Carrasco S, Picatoste B, Benito-Martin A, Zubiri I, Sanz AB, Sanchez-Nino MD, Ortiz A, Egido J, Tunon J, Lorenzo O. Myocardial fibrosis and apoptosis, but not inflammation, are present in long-term experimental diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297: H2109–H2119, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Baines CP. The cardiac mitochondrion: nexus of stress. Annu Rev Physiol 72: 61–80, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

