Participation of the p38 pathway in Drosophila host defense against pathogenic bacteria and fungi
- PMID: 21076039
- PMCID: PMC2996427
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1009223107
Participation of the p38 pathway in Drosophila host defense against pathogenic bacteria and fungi
Abstract
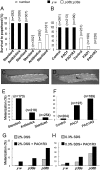
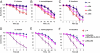
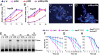
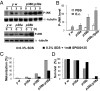
The signaling network of innate immunity in Drosophila is constructed by multiple evolutionarily conserved pathways, including the Toll- or Imd-regulated NF-κB and JNK pathways. The p38 MAPK pathway is evolutionarily conserved in stress responses, but its role in Drosophila host defense is not fully understood. Here we show that the p38 pathway also participates in Drosophila host defense. In comparison with wild-type flies, the sensitivity to microbial infection was slightly higher in the p38a mutant, significantly higher in the p38b mutant, but unchanged in the p38c mutant. The p38b;p38a double-mutant flies were hypersensitive to septic injury. The immunodeficiency of p38b;p38a mutant flies was also demonstrated by hindgut melanization and larvae stage lethality that were induced by microbes naturally presented in fly food. A canonical MAP3K-MKK cascade was found to mediate p38 activation in response to infection in flies. However, neither Toll nor Imd was required for microbe-induced p38 activation. We found that p38-activated heat-shock factor and suppressed JNK collectively contributed to host defense against infection. Together, our data demonstrate that the p38 pathway-mediated stress response contribute to Drosophila host defense against microbial infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A member of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase family is responsible for transcriptional induction of Dopa decarboxylase in the epidermis of Drosophila melanogaster during the innate immune response.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Aug;28(15):4883-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02074-07. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18519585 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles of p38 and JNK in a Drosophila model of TDP-43 proteinopathy reveal oxidative stress and innate immunity as pathogenic components of neurodegeneration.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Feb 1;24(3):757-72. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu493. Epub 2014 Oct 3. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25281658 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila MAPK p38c regulates oxidative stress and lipid homeostasis in the intestine.PLoS Genet. 2014 Sep 25;10(9):e1004659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004659. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25254641 Free PMC article.
-
Stress signaling in Drosophila.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 1;18(45):6172-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203125. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10557109 Review.
-
NF-kappaB in the immune response of Drosophila.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009 Dec;1(6):a000232. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000232. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009. PMID: 20457557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Drosophila melanogaster host model.J Oral Microbiol. 2012;4. doi: 10.3402/jom.v4i0.10368. Epub 2012 Feb 21. J Oral Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22368770 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Hippo signalling by p38 signalling.J Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Aug;8(4):328-37. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjw036. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27402810 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular tug of war between immunity and fertility: Emergence of conserved signaling pathways and regulatory mechanisms.Bioessays. 2020 Dec;42(12):e2000103. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000103. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Bioessays. 2020. PMID: 33169418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prolonged Transcriptional Consequences in Survivors of Sepsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 21;22(11):5422. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115422. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34063857 Free PMC article.
-
Symbiosis with Francisella tularensis provides resistance to pathogens in the silkworm.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 10;6:31476. doi: 10.1038/srep31476. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27507264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imler JL, Hoffmann JA. Toll receptors in Drosophila: A family of molecules regulating development and immunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002;270:63–79. - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spätzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell. 1996;86:973–983. - PubMed
-
- Hedengren M, et al. Relish, a central factor in the control of humoral but not cellular immunity in Drosophila. Mol Cell. 1999;4:827–837. - PubMed
-
- Silverman N, Maniatis T. NF-kappaB signaling pathways in mammalian and insect innate immunity. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2321–2342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

