A brief culturally tailored intervention for Puerto Ricans with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 21076128
- PMCID: PMC3082938
- DOI: 10.1177/1090198110366004
A brief culturally tailored intervention for Puerto Ricans with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
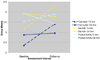
The information-motivation-behavioral skills (IMB) model of health behavior change informed the design of a brief, culturally tailored diabetes self-care intervention for Puerto Ricans with type 2 diabetes. Participants (n = 118) were recruited from an outpatient, primary care clinic at an urban hospital in the northeast United States. ANCOVA models evaluated intervention effects on food label reading, diet adherence, physical activity, and glycemic control (HbA1c). At follow-up, the intervention group was reading food labels and adhering to diet recommendations significantly more than the control group. Although the mean HbA1c values decreased in both groups (
Intervention: 0.48% vs.
Control: 0.27% absolute decrease), only the intervention group showed a significant improvement from baseline to follow-up (p < .008), corroborating improvements in diabetes self-care behaviors. Findings support the use of the IMB model to culturally tailor diabetes interventions and to enhance patients' knowledge, motivation, and behavior skills needed for self-care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adams CR. Lessons learned from urban Latinas with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Transcultural Nursing. 2003;14(3):255–265. - PubMed
-
- Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes. Special Issue: Theories of cognitive self-regulation. 1991;50(2):179–211.
-
- Ajzen I, Fishbein M. The influence of attitudes on behavior. In: Albarracin D, Johnson BT, Zanna MP, editors. The handbook of attitudes. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2005. pp. 173–221.
-
- Anderson RM, Funnell MM, Nwankwo R, Gillard ML, Oh M, Fitzgerald JT. Evaluating a problem-based empowerment program for African Americans with diabetes: results of a randomized controlled trial. Ethnicity and Disease. 2005;15(4):671–678. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A. Human agency in social cognitive theory. The American Psychologist. 1989;44(9):1175–1184. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical