An analytic model of neutron ambient dose equivalent and equivalent dose for proton radiotherapy
- PMID: 21076197
- PMCID: PMC3001300
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/23/S01
An analytic model of neutron ambient dose equivalent and equivalent dose for proton radiotherapy
Abstract
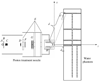
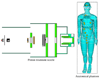
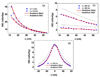
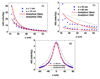
Stray neutrons generated in passively scattered proton therapy are of concern because they increase the risk that a patient will develop a second cancer. Several investigations characterized stray neutrons in proton therapy using experimental measurements and Monte Carlo simulations, but capabilities of analytical methods to predict neutron exposures are less well developed. The goal of this study was to develop a new analytical model to calculate neutron ambient dose equivalent in air and equivalent dose in phantom based on Monte Carlo modeling of a passively scattered proton therapy unit. The accuracy of the new analytical model is superior to a previous analytical model and comparable to the accuracy of typical Monte Carlo simulations and measurements. Predictions from the new analytical model agreed reasonably well with corresponding values predicted by a Monte Carlo code using an anthropomorphic phantom.
Figures
References
-
- Agosteo S, Birattari C, Caravaggio M, Silari M, Tosi G. Secondary neutron and photon dose in proton therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 1998;48:293–305. - PubMed
-
- Athar BS, Paganetti H. Neutron dose equivalents and associated lifetime cancer incidence risks for head and neck and spinal proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009;54:4907–4926. - PubMed
-
- Billings MP, Yucker WR. Report MDC G4655. Huntington Beach, CA: McDonnell Douglas Corporation; 1973. Summary final report: the computerized anatomical man (CAM)
-
- Binns PJ, Hough JH. Secondary dose exposures during 200 MeV proton therapy. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1997;70:441–444.
-
- Fontenot J, Taddei P, Zheng Y, Mirkovic D, Jordan T, Newhauser W. Dose equivalent and effective dose from stray radiation during passively scattered proton radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008;53:1677–1688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
