Common variants in 22 loci are associated with QRS duration and cardiac ventricular conduction
- PMID: 21076409
- PMCID: PMC3338195
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.716
Common variants in 22 loci are associated with QRS duration and cardiac ventricular conduction
Abstract
The QRS interval, from the beginning of the Q wave to the end of the S wave on an electrocardiogram, reflects ventricular depolarization and conduction time and is a risk factor for mortality, sudden death and heart failure. We performed a genome-wide association meta-analysis in 40,407 individuals of European descent from 14 studies, with further genotyping in 7,170 additional Europeans, and we identified 22 loci associated with QRS duration (P < 5 × 10(-8)). These loci map in or near genes in pathways with established roles in ventricular conduction such as sodium channels, transcription factors and calcium-handling proteins, but also point to previously unidentified biologic processes, such as kinase inhibitors and genes related to tumorigenesis. We demonstrate that SCN10A, a candidate gene at the most significantly associated locus in this study, is expressed in the mouse ventricular conduction system, and treatment with a selective SCN10A blocker prolongs QRS duration. These findings extend our current knowledge of ventricular depolarization and conduction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
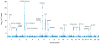
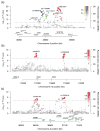
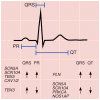

Comment in
-
Genetics: Meta-analysis identifies variants in 22 loci associated with QRS duration.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011 Feb;8(2):63. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.214. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21348140 No abstract available.
References
-
- Desai AD, et al. Prognostic Significance of Quantitative QRS Duration. Am J Med. 2006;119:600–606. - PubMed
-
- Elhendy A, Hammill SC, Mahoney DW, Pellikka PA. Relation of QRS duration on the surface 12-lead electrocardiogram with mortality in patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96:1082–1088. - PubMed
-
- Oikarinen L, et al. QRS duration and QT interval predict mortality in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: the Losartan Intervention for Endpoint Reduction in Hypertension Study. Hypertension. 2004;43:1029–1034. - PubMed
-
- Dhingra R, et al. Electrocardiographic QRS duration and the risk of congestive heart failure: the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension. 2006;47:861–867. - PubMed
-
- Busjahn A, et al. QT interval is linked to 2 long-QT syndrome loci in normal subjects. Circulation. 1999;99:3161–3164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0400874/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- SP/08/005/25115/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- U01HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL082727/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55018/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL64757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N02-HL-6-4278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- G9521010/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HL80025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL59367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55022/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23HL80025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-55016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/02/128/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- NS058980/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200625226C/PHS HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55021/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088456/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-35129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 HL097675/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55019/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G9521010D/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 06/094/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55020/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-15103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G20234/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/07/005/23633/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AG-12100/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/B/04/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom

