Chemoenzymatic syntheses and anti-HIV-1 activity of glucose-nucleoside conjugates as prodrugs
- PMID: 21077659
- PMCID: PMC3070195
- DOI: 10.1021/bc1002168
Chemoenzymatic syntheses and anti-HIV-1 activity of glucose-nucleoside conjugates as prodrugs
Abstract
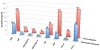
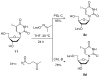
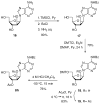
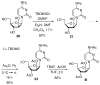
Phosphodiester linked conjugates of various nucleosides such as d4U, d4T, IdUrd, ddI, ddA, virazole, ara-A, and ara-C containing a glucosyl moiety have been described. These compounds were designed to act as prodrugs, where the corresponding 5'-monophosphates may be generated intracellularly. The synthesis of the glycoconjugates was achieved in good yields by condensation of a glucosyl phosphoramidite 7 with nucleosides in the presence of an activating agent. It was demonstrated that the glucose conjugates improve the water solubility of the nucleoside analogues, for example, up to 31-fold for the ara-A conjugate compared to that of ara-A alone. The new conjugates were tested for their anti-HIV-1 activity in human lymphocytes. These derivatives offer a convenient design for potential prodrug candidates with the possibility of improving the physicochemical properties and therapeutic activity of nucleoside analogues.
Figures





References
-
- Schinazi RF, Liotta DC. Frontiers in Nucleoside and Nucleic Acids. IHL Press; Tucker, Georgia: 2004.
-
- Rachakonda S, Cartee L. Challenges in Antimicrobial Drug Discovery and the Potential of Nucleoside Antibiotics. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11:775–793. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq E. Antiviral drugs in current clinical use. J Clin Vir. 2004;30:115–133. - PubMed
-
- Chu CK. Recent Advances in Nucleosides: Chemistry and Chemotherapy. Elsevier Science; New York: 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

