Phase I/II study of a 3-week cycle of irinotecan and S-1 in patients with advanced colorectal cancer
- PMID: 21077997
- PMCID: PMC11158519
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01728.x
Phase I/II study of a 3-week cycle of irinotecan and S-1 in patients with advanced colorectal cancer
Abstract
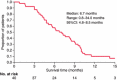
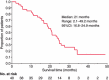
The combination of an oral fluoropyrimidine derivative, S-1, and irinotecan is expected to be a promising regimen for advanced colorectal cancer. This study was performed to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended dose (RD) of irinotecan combined with S-1 in a 3-week cycle regimen and to observe the safety and efficacy for patients with previously untreated advanced colorectal cancer. Eighty milligrams per m(2) of S-1 was given orally for 14 consecutive days and escalated doses of irinotecan were administered on days 1 and 8 every 3 weeks in the phase I trial. Forty patients were treated at the RD during the phase II trial. Forty-three patients were enrolled between February 2005 and March 2007. The dose-limiting toxicity was diarrhea and abdominal pain. The MTD of irinotecan was 100 mg/m(2) and the RD was determined to be 80 mg/m(2) of irinotecan combined with 80 mg/m(2) of S-1. The phase II trial showed that 22 of 40 patients achieved a complete or partial response and eight had stable disease. The overall response rate was 55.0%. The median progression-free survival time and median survival time were 6.7 and 21 months, respectively. There were no treatment-related deaths. The main toxicities were leukopenia, neutropenia, anorexia and diarrhea. This study suggests the combination of irinotecan and S-1 repeated every 3 weeks is tolerable and effective for patients with previously untreated advanced colorectal cancer.
© 2010 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase I study of bevacizumab combined with irinotecan and S-1 as second-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Jan;71(1):29-34. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-2023-7. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23228984 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I/II study of oral uracil/tegafur (UFT), leucovorin and irinotecan in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.Ann Oncol. 2003 Aug;14(8):1264-9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdg340. Ann Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12881390 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II study of combination therapy with S-1 and irinotecan in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.Ann Oncol. 2006 Jun;17(6):968-73. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdl066. Epub 2006 Apr 7. Ann Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16603600 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I/II study of S-1 combined with irinotecan for metastatic advanced gastric cancer.Br J Cancer. 2006 Apr 24;94(8):1130-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603072. Br J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16570038 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[The current evidence of S-1 and irinotecan hydrochloride combination chemotherapy with tri-weekly schedule].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2006 Jun;33 Suppl 1:125-30. doi: 10.2217/14750708.3.1.125. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2006. PMID: 16897987 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Comparison of short-term efficacy and safety of TIROX and DCF regimens for advanced gastric cancer.J Int Med Res. 2014 Jun;42(3):737-43. doi: 10.1177/0300060513510657. Epub 2014 Apr 9. J Int Med Res. 2014. PMID: 24717407 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
REDOMA: Bayesian random-effects dose-optimization meta-analysis using spike-and-slab priors.Stat Med. 2024 Aug 15;43(18):3484-3502. doi: 10.1002/sim.10107. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Stat Med. 2024. PMID: 38857904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimada Y, Yoshino M, Wakui A et al. Phase II study of CPT‐11, a new camptothecin derivative, in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 1993; 11: 909–13. - PubMed
-
- Pavillard V, Formento P, Rostagno P et al. Combination of irinotecan (CPT‐11) and 5‐fluorouracil with an analysis of cellular determinants of drug activity. Biochem Pharmacol 1998; 56: 1315–22. - PubMed
-
- Mullany S, Svingen PA, Kaufmann SH et al. Effect of adding the topoisomerase I poison 7‐ethyl‐10‐hydroxycamptothecin (SN‐38) to 5‐fluorouracil and folinic acid in HCT‐8 cells: elevated dTTP pools and enhanced cytotoxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1998; 42: 391–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

