Targeting of B and T lymphocyte associated (BTLA) prevents graft-versus-host disease without global immunosuppression
- PMID: 21078889
- PMCID: PMC2989771
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20102017
Targeting of B and T lymphocyte associated (BTLA) prevents graft-versus-host disease without global immunosuppression
Abstract
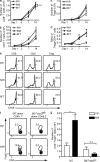
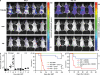
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) causes significant morbidity and mortality in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (aHSCT), preventing its broader application to non-life-threatening diseases. We show that a single administration of a nondepleting monoclonal antibody specific for the coinhibitory immunoglobulin receptor, B and T lymphocyte associated (BTLA), permanently prevented GVHD when administered at the time of aHSCT. Once GVHD was established, anti-BTLA treatment was unable to reverse disease, suggesting that its mechanism occurs early after aHSCT. Anti-BTLA treatment prevented GVHD independently of its ligand, the costimulatory tumor necrosis factor receptor herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), and required BTLA expression by donor-derived T cells. Furthermore, anti-BTLA treatment led to the relative inhibition of CD4(+) forkhead box P3(-) (Foxp3(-)) effector T cell (T eff cell) expansion compared with precommitted naturally occurring donor-derived CD4(+) Foxp3(+) regulatory T cell (T reg cell) and allowed for graft-versus-tumor (GVT) effects as well as robust responses to pathogens. These results suggest that BTLA agonism rebalances T cell expansion in lymphopenic hosts after aHSCT, thereby preventing GVHD without global immunosuppression. Thus, targeting BTLA with a monoclonal antibody at the initiation of aHSCT therapy might reduce limitations imposed by histocompatibility and allow broader application to treatment of non-life-threatening diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Blazar B.R., Carreno B.M., Panoskaltsis-Mortari A., Carter L., Iwai Y., Yagita H., Nishimura H., Taylor P.A. 2003. Blockade of programmed death-1 engagement accelerates graft-versus-host disease lethality by an IFN-gamma-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 171:1272–1277 - PubMed
-
- Cooke K.R., Kobzik L., Martin T.R., Brewer J., Delmonte J., Jr, Crawford J.M., Ferrara J.L.M. 1996. An experimental model of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after bone marrow transplantation: I. The roles of minor H antigens and endotoxin. Blood. 88:3230–3239 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

