Downstream of tyrosine kinase 1 and 2 play opposing roles in CD200 receptor signaling
- PMID: 21078907
- PMCID: PMC2999833
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002858
Downstream of tyrosine kinase 1 and 2 play opposing roles in CD200 receptor signaling
Abstract
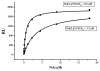
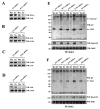
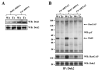
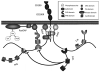
The CD200 receptor (CD200R) negatively regulates myeloid cells by interacting with its widely expressed ligand CD200. CD200R signals through a unique inhibitory pathway involving a direct interaction with the adaptor protein downstream of tyrosine kinase 2 (Dok2) and the subsequent recruitment and activation of Ras GTPase-activating protein (RasGAP). Ligand engagement of CD200R also results in tyrosine phosphorylation of Dok1, but this protein is not essential for inhibitory CD200R signaling in human myeloid cells. In this paper, we show that CD200R-induced phosphorylation of Dok2 precedes phosphorylation of Dok1, and that Dok2 and Dok1 recruit different downstream proteins. Compared with Dok2, Dok1 recruits substantially less RasGAP. In addition to binding RasGAP, Dok2 recruits the adaptor molecule Nck in response to ligand engagement of CD200R. CD200R-induced phosphorylation of Dok1 results in the recruitment of CT10 sarcoma oncogene cellular homologue-like (CrkL), whereas the closely related CT10 sarcoma oncogene cellular homologue interacts constitutively with Dok1. Knockdown of Dok1 or CrkL expression in U937 cells resulted in increased Dok2 phosphorylation and RasGAP recruitment to Dok2. These data are consistent with a model in which Dok1 negatively regulates Dok2-mediated CD200R signaling through the recruitment of CrkL.
Figures
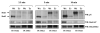
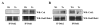
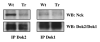
Similar articles
-
Essential roles for Dok2 and RasGAP in CD200 receptor-mediated regulation of human myeloid cells.J Immunol. 2009 Oct 15;183(8):4879-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901531. Epub 2009 Sep 28. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19786546 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of CD200 inhibition of mast cell activation.J Immunol. 2004 Dec 1;173(11):6786-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.11.6786. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15557172
-
Differential role of Dok1 and Dok2 in TLR2-induced inflammatory signaling in glia.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:148-58. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.04.007. Epub 2013 May 7. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23659921
-
The roles of Dok family adapters in immunoreceptor signaling.Immunol Rev. 2009 Nov;232(1):273-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00844.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19909370 Review.
-
Is the CD200/CD200 receptor interaction more than just a myeloid cell inhibitory signal?Crit Rev Immunol. 2006;26(3):213-30. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v26.i3.20. Crit Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16928187 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the innate immune cells during pregnancy: An immune checkpoint perspective.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(22):10362-10375. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17022. Epub 2021 Oct 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34708495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Introduction to DOK2 and its potential role in cancer.Physiol Res. 2021 Nov 29;70(5):671-685. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934710. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 34505522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic infection drives expression of the inhibitory receptor CD200R, and its ligand CD200, by mouse and human CD4 T cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035466. Epub 2012 Apr 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22496920 Free PMC article.
-
Dissection of agonistic and blocking effects of CD200 receptor antibodies.PLoS One. 2013 May 14;8(5):e63325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063325. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691022 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing the Inflammatory Response to Clinically Relevant Polymers by Manipulating the Host Response Using ITIM Domain-Containing Receptors.Polymers (Basel). 2014 Sep 29;6(10):2526-2551. doi: 10.3390/polym6102526. Polymers (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25705515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wright GJ, Puklavec MJ, Willis AC, Hoek RM, Sedgwick JD, Brown MH, Barclay AN. Lymphoid/neuronal cell surface OX2 glycoprotein recognizes a novel receptor on macrophages implicated in the control of their function. Immunity. 2000;13:233–242. - PubMed
-
- Wright GJ, Cherwinski H, Foster-Cuevas M, Brooke G, Puklavec MJ, Bigler M, Song Y, Jenmalm M, Gorman D, McClanahan T, Liu MR, Brown MH, Sedgwick JD, Phillips JH, Barclay AN. Characterization of the CD200 receptor family in mice and humans and their interactions with CD200. J. Immunol. 2003;171:3034–3046. - PubMed
-
- Cherwinski HM, Murphy CA, Joyce BL, Bigler ME, Song YS, Zurawski SM, Moshrefi MM, Gorman DM, Miller KL, Zhang S, Sedgwick JD, Phillips JH. The CD200 receptor is a novel and potent regulator of murine and human mast cell function. J. Immunol. 2005;174:1348–1356. - PubMed
-
- Jenmalm MC, Cherwinski H, Bowman EP, Phillips JH, Sedgwick JD. Regulation of myeloid cell function through the CD200 receptor. J. Immunol. 2006;176:191–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

