RNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of DNA copy number
- PMID: 21078984
- PMCID: PMC3009799
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1012236107
RNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of DNA copy number
Abstract
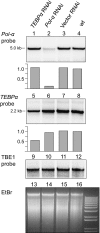
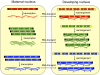
Increasing evidence suggests that parentally supplied RNA plays crucial roles during eukaryotic development. This epigenetic contribution may regulate gene expression from the earliest stages. Although present in a variety of eukaryotes, maternally inherited characters are especially prominent in ciliated protozoa, in which parental noncoding RNA molecules instruct whole-genome reorganization. This includes removal of nearly all noncoding DNA and sorting the remaining fragments, producing extremely gene-rich somatic genomes. Chromosome fragmentation and extensive replication produce variable DNA copy numbers in the somatic genome. Understanding the forces that drive and regulate copy number change is fundamental. We show that RNA molecules present in parental cells during sexual reproduction can regulate chromosome copy number in the developing nucleus of the ciliate Oxytricha. Experimentally induced changes in RNA abundance can both increase and decrease the levels of corresponding DNA molecules in progeny, demonstrating epigenetic inheritance of chromosome copy number. These results suggest that maternal RNA, in addition to controlling gene expression or DNA processing, can also program DNA amplification levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Modulating somatic DNA copy number through maternal RNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Dec 21;107(51):21951-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017135108. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21149732 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Emerson JJ, Cardoso-Moreira M, Borevitz JO, Long M. Natural selection shapes genome-wide patterns of copy-number polymorphism in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2008;320:1629–1631. - PubMed
-
- Cooper GM, Nickerson DA, Eichler EE. Mutational and selective effects on copy-number variants in the human genome. Nat Genet. 2007;39(7 suppl):S22–S29. - PubMed
-
- Hyman E, et al. Impact of DNA amplification on gene expression patterns in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6240–6245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

