Neutrophil elastase, proteinase 3, and cathepsin G as therapeutic targets in human diseases
- PMID: 21079042
- PMCID: PMC2993259
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.110.002733
Neutrophil elastase, proteinase 3, and cathepsin G as therapeutic targets in human diseases
Abstract
Polymorphonuclear neutrophils are the first cells recruited to inflammatory sites and form the earliest line of defense against invading microorganisms. Neutrophil elastase, proteinase 3, and cathepsin G are three hematopoietic serine proteases stored in large quantities in neutrophil cytoplasmic azurophilic granules. They act in combination with reactive oxygen species to help degrade engulfed microorganisms inside phagolysosomes. These proteases are also externalized in an active form during neutrophil activation at inflammatory sites, thus contributing to the regulation of inflammatory and immune responses. As multifunctional proteases, they also play a regulatory role in noninfectious inflammatory diseases. Mutations in the ELA2/ELANE gene, encoding neutrophil elastase, are the cause of human congenital neutropenia. Neutrophil membrane-bound proteinase 3 serves as an autoantigen in Wegener granulomatosis, a systemic autoimmune vasculitis. All three proteases are affected by mutations of the gene (CTSC) encoding dipeptidyl peptidase I, a protease required for activation of their proform before storage in cytoplasmic granules. Mutations of CTSC cause Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome. Because of their roles in host defense and disease, elastase, proteinase 3, and cathepsin G are of interest as potential therapeutic targets. In this review, we describe the physicochemical functions of these proteases, toward a goal of better delineating their role in human diseases and identifying new therapeutic strategies based on the modulation of their bioavailability and activity. We also describe how nonhuman primate experimental models could assist with testing the efficacy of proposed therapeutic strategies.
Figures

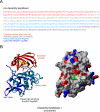
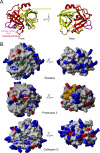
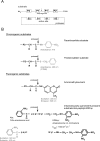

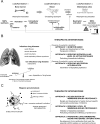
References
-
- Abraham CR, Selkoe DJ, Potter H. (1988) Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell 52:487–501 - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801 - PubMed
-
- Akita K, Ohtsuki T, Nukada Y, Tanimoto T, Namba M, Okura T, Takakura-Yamamoto R, Torigoe K, Gu Y, Su MS, et al. (1997) Involvement of caspase-1 and caspase-3 in the production and processing of mature human interleukin 18 in monocytic THP.1 cells. J Biol Chem 272:26595–26603 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

