Drug-induced long QT syndrome
- PMID: 21079043
- PMCID: PMC2993258
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.110.003723
Drug-induced long QT syndrome
Abstract
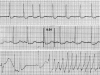
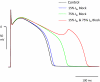
The drug-induced long QT syndrome is a distinct clinical entity that has evolved from an electrophysiologic curiosity to a centerpiece in drug regulation and development. This evolution reflects an increasing recognition that a rare adverse drug effect can profoundly upset the balance between benefit and risk that goes into the prescription of a drug by an individual practitioner as well as the approval of a new drug entity by a regulatory agency. This review will outline how defining the central mechanism, block of the cardiac delayed-rectifier potassium current I(Kr), has contributed to defining risk in patients and in populations. Models for studying risk, and understanding the way in which clinical risk factors modulate cardiac repolarization at the molecular level are discussed. Finally, the role of genetic variants in modulating risk is described.
Figures

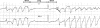


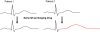
References
-
- Abbott GW, Sesti F, Splawski I, Buck ME, Lehmann MH, Timothy KW, Keating MT, Goldstein SA. (1999) MiRP1 forms IKr potassium channels with HERG and is associated with cardiac arrhythmia. Cell 97:175–187 - PubMed
-
- Abrahamsson C, Palmer M, Ljung B, Duker G, Bäärnhielm C, Carlsson L, Danielsson B. (1994) Induction of rhythm abnormalities in the fetal rat heart. A tentative mechanism for the embryotoxic effect of the class III antiarrhythmic agent almokalant. Cardiovasc Res 28:337–344 - PubMed
-
- Aiba T, Shimizu W, Inagaki M, Noda T, Miyoshi S, Ding WG, Zankov DP, Toyoda F, Matsuura H, Horie M, et al. (2005) Cellular and ionic mechanism for drug-induced long QT syndrome and effectiveness of verapamil. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:300–307 - PubMed
-
- Albert CM, Nam EG, Rimm EB, Jin HW, Hajjar RJ, Hunter DJ, MacRae CA, Ellinor PT. (2008) Cardiac sodium channel gene variants and sudden cardiac death in women. Circulation 117:16–23 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

