Plk1 negatively regulates Cep55 recruitment to the midbody to ensure orderly abscission
- PMID: 21079244
- PMCID: PMC2983065
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201008108
Plk1 negatively regulates Cep55 recruitment to the midbody to ensure orderly abscission
Abstract
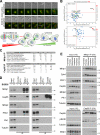
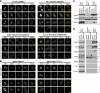
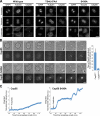
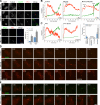
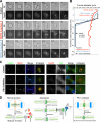
Cytokinesis requires a membrane-remodeling and fission event termed abscission that occurs after chromosome segregation, cleavage furrow formation, and contraction have completed. In this study, we show how abscission factor recruitment is controlled by the Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1). At the metaphase-anaphase transition, Plk1 initiates cleavage furrow formation and is then progressively degraded during mitotic exit. During this period, Plk1 phosphorylates the abscission factor Cep55 in trans and prevents its untimely recruitment to the anaphase spindle. A Plk1 phosphorylation site mutant of Cep55 is prematurely recruited to the anaphase spindle and fails to support abscission. Endogenous Cep55 behaves similarly after Plk1 inhibition by the drugs BI2536 or GW842862. Only once Plk1 is degraded can Cep55 target to the midbody and promote abscission. Blocking Plk1 degradation leads to elevated levels of Plk1 at the midbody and the failure of Cep55 recruitment. Thus, Plk1 activity negatively regulates Cep55 to ensure orderly abscission factor recruitment and ensures that this occurs only once cell contraction has completed.
Figures
References
-
- Burkard M.E., Randall C.L., Larochelle S., Zhang C., Shokat K.M., Fisher R.P., Jallepalli P.V. 2007. Chemical genetics reveals the requirement for Polo-like kinase 1 activity in positioning RhoA and triggering cytokinesis in human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 104:4383–4388 10.1073/pnas.0701140104 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burkard M.E., Maciejowski J., Rodriguez-Bravo V., Repka M., Lowery D.M., Clauser K.R., Zhang C., Shokat K.M., Carr S.A., Yaffe M.B., Jallepalli P.V. 2009. Plk1 self-organization and priming phosphorylation of HsCYK-4 at the spindle midzone regulate the onset of division in human cells. PLoS Biol. 7:e1000111 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000111 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

