Association of isoniazid preventive therapy with lower early mortality in individuals on antiretroviral therapy in a workplace programme
- PMID: 21079429
- PMCID: PMC3724406
- DOI: 10.1097/01.aids.0000391010.02774.6f
Association of isoniazid preventive therapy with lower early mortality in individuals on antiretroviral therapy in a workplace programme
Abstract
Objective: To describe the association between isoniazid preventive therapy (IPT) and mortality among individuals starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) in a workplace programme in South Africa where tuberculosis (TB) incidence is very high.
Methods: ART-naive individuals starting ART from January 2004 to December 2007 were followed for up to 12 months. Deaths were ascertained from clinic and human resource data. The association between IPT and mortality was assessed using Cox regression.
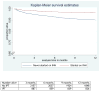
Results: A total of 3270 individuals were included (median age 45; 93% men; median baseline CD4 cell count 155 cells/μl (interquartile range 87-221); and 45% with WHO stage 3/4]. Nine hundred twenty-two (28%) individuals started IPT either prior to or within 3 months of starting ART. Individuals who started IPT tended to have less advanced HIV disease at ART initiation. Two hundred fifty-nine (7.9%) deaths were observed with overall mortality rate 8.9 per 100 person-years [95% confidence interval (CI) 7.9-10.6]. The unadjusted mortality rate was lower among those who received IPT compared with those who did not [3.7/100 vs. 11.1/100 person-years, respectively, hazard ratio 0.34 (95% CI 0.24-0.49)]; this association remained after adjustment for age, baseline CD4 cell count, baseline WHO stage, year of ART start, and individual company (hazard ratio 0.51, 95% CI 0.32-0.80). In sensitivity analyses restricted to those with no previous history of TB (n = 3036) or with no TB symptoms at ART initiation (n = 2251), IPT remained associated with reduced mortality [adjusted hazard ratios 0.51 (95% CI 0.32-0.81) and 0.48 (95% CI 0.24-0.96), respectively].
Conclusion: Mortality was lower among individuals receiving IPT with or prior to ART start. These results support routine use of IPT in conjunction with ART.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Why have trials of isoniazid preventive therapy among people with HIV infection not demonstrated an effect on mortality?: did close examination of the trees obscure our view of the wood?AIDS. 2010 Nov;24 Suppl 5:S15-8. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000391011.40892.ff. AIDS. 2010. PMID: 21079423 No abstract available.
-
Reducing tuberculosis-associated early mortality in antiretroviral treatment programmes in sub-Saharan Africa.AIDS. 2011 Jul 31;25(12):1554-5; author reply 1556. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328348fb61. AIDS. 2011. PMID: 21747238 No abstract available.
References
-
- Braitstein P, Brinkhof MW, Dabis F, Schechter M, Boulle A, Miotti P, et al. Mortality of HIV-1-infected patients in the first year of antiretroviral therapy: comparison between low-income and high-income countries. Lancet. 2006;367:817–824. - PubMed
-
- Lawn SD, Myer L, Harling G, Orrell C, Bekker LG, Wood R. Determinants of mortality and nondeath losses from an antiretroviral treatment service in South Africa: implications for program evaluation. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Lucas SB, Hounnou A, Peacock C, Beaumel A, Djomand G, N’Gbichi JM, et al. The mortality and pathology of HIV infection in a west African city. AIDS. 1993;7:1569–1579. - PubMed
-
- Grant AD, Djomand G, De Cock KM. Natural history and spectrum of disease in adults with HIV/AIDS in Africa. AIDS. 1997;11 (Suppl B):S43–54. - PubMed
-
- Badri M, Wilson D, Wood R. Effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy on incidence of tuberculosis in South Africa: a cohort study. Lancet. 2002;359:2059–2064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials