Gene expression patterns in the hippocampus and amygdala of endogenous depression and chronic stress models
- PMID: 21079605
- PMCID: PMC3117129
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2010.119
Gene expression patterns in the hippocampus and amygdala of endogenous depression and chronic stress models
Abstract
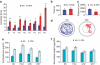
The etiology of depression is still poorly understood, but two major causative hypotheses have been put forth: the monoamine deficiency and the stress hypotheses of depression. We evaluate these hypotheses using animal models of endogenous depression and chronic stress. The endogenously depressed rat and its control strain were developed by bidirectional selective breeding from the Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rat, an accepted model of major depressive disorder (MDD). The WKY More Immobile (WMI) substrain shows high immobility/despair-like behavior in the forced swim test (FST), while the control substrain, WKY Less Immobile (WLI), shows no depressive behavior in the FST. Chronic stress responses were investigated by using Brown Norway, Fischer 344, Lewis and WKY, genetically and behaviorally distinct strains of rats. Animals were either not stressed (NS) or exposed to chronic restraint stress (CRS). Genome-wide microarray analyses identified differentially expressed genes in hippocampi and amygdalae of the endogenous depression and the chronic stress models. No significant difference was observed in the expression of monoaminergic transmission-related genes in either model. Furthermore, very few genes showed overlapping changes in the WMI vs WLI and CRS vs NS comparisons, strongly suggesting divergence between endogenous depressive behavior- and chronic stress-related molecular mechanisms. Taken together, these results posit that although chronic stress may induce depressive behavior, its molecular underpinnings differ from those of endogenous depression in animals and possibly in humans, suggesting the need for different treatments. The identification of novel endogenous depression-related and chronic stress response genes suggests that unexplored molecular mechanisms could be targeted for the development of novel therapeutic agents.
Figures

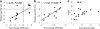
References
-
- Rumsfeld JS, Ho PM. Depression and cardiovascular disease: a call for recognition. Circulation. 2005;111:250–253. - PubMed
-
- Swaab DF, Bao AM, Lucassen PJ. The stress system in the human brain in depression and neurodegeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2005;4:141–194. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein SR, Schuppenies A, Wong ML, Licinio J. Approaching the shared biology of obesity and depression: the stress axis as the locus of gene–environment interactions. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11:892–902. - PubMed
-
- Kessler RC, Ormel J, Demler O, Stang PE. Comorbid mental disorders account for the role impairment of commonly occurring chronic physical disorders: results from the National Comorbidity Survey. J Occup Environ Med. 2003;45:1257–1266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

