Anti-tumor effect in human lung cancer by a combination treatment of novel histone deacetylase inhibitors: SL142 or SL325 and retinoic acids
- PMID: 21079797
- PMCID: PMC2973950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013834
Anti-tumor effect in human lung cancer by a combination treatment of novel histone deacetylase inhibitors: SL142 or SL325 and retinoic acids
Abstract
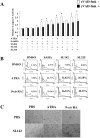
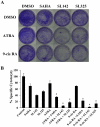
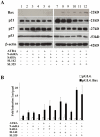
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors arrest cancer cell growth and cause apoptosis with low toxicity thereby constituting a promising treatment for cancer. In this study, we investigated the anti-tumor activity in lung cancer cells of the novel cyclic amide-bearing hydroxamic acid based HDAC inhibitors SL142 and SL325. In A549 and H441 lung cancer cells both SL142 and SL325 induced more cell growth inhibition and cell death than the hydroxamic acid-based HDAC inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA). Moreover, the combination treatment using retinoid drugs ATRA or 9-cis RA along with SL142 or SL325 significantly induced more apoptosis and suppressed colony formation than the single use of either. The expression of the retinoic acid receptors RARα, RARβ, RXRα and RXRβ were unchanged with the treatment. However a luciferase reporter construct (pGL4. RARE 7x) containing seven tandem repeats of the retinoic acid responsible element (RARE) generated significant transcriptional activity after the combination treatment of retinoic acids and SL142 or SL325 in H441 lung cancer cells. Moreover, apoptosis-promoting Bax expression and caspase-3 activity was increased after the combination treatment. These results suggest that the combination treatment of SL142 or SL325 with retinoic acids exerts significant anti-tumor activity and is a promising therapeutic candidate to treat human lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Struhl K. Histone acetylation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1998;12:599–606. - PubMed
-
- Rosato RR, Grant S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2:30–37. - PubMed
-
- Muraoka M, Konishi M, Kikuchi-Yanoshita R, Tanaka K, Shitara N, et al. p300 gene alterations in colorectal and gastric carcinomas. Oncogene. 1996;12:1565–1569. - PubMed
-
- He LZ, Guidez F, Tribioli C, Peruzzi D, Ruthardt M, et al. Distinct interactions of PML-RARalpha and PLZF-RARalpha with co-repressors determine differential responses to RA in APL. Nat Genet. 1998;18:126–135. - PubMed
-
- Grignani F, De Matteis S, Nervi C, Tomassoni L, Gelmetti V, et al. Fusion proteins of the retinoic acid receptor-alpha recruit histone deacetylase in promyelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1998;391:815–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

