Highly efficient purification of protein complexes from mammalian cells using a novel streptavidin-binding peptide and hexahistidine tandem tag system: application to Bruton's tyrosine kinase
- PMID: 21080425
- PMCID: PMC3047070
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.546
Highly efficient purification of protein complexes from mammalian cells using a novel streptavidin-binding peptide and hexahistidine tandem tag system: application to Bruton's tyrosine kinase
Abstract
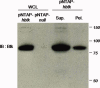
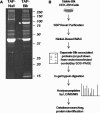
Tandem affinity purification (TAP) is a generic approach for the purification of protein complexes. The key advantage of TAP is the engineering of dual affinity tags that, when attached to the protein of interest, allow purification of the target protein along with its binding partners through two consecutive purification steps. The tandem tag used in the original method consists of two IgG-binding units of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus (ProtA) and the calmodulin-binding peptide (CBP), and it allows for recovery of 20-30% of the bait protein in yeast. When applied to higher eukaryotes, however, this classical TAP tag suffers from low yields. To improve protein recovery in systems other than yeast, we describe herein the development of a three-tag system comprised of CBP, streptavidin-binding peptide (SBP) and hexa-histidine. We illustrate the application of this approach for the purification of human Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk), which results in highly efficient binding and elution of bait protein in both purification steps (>50% recovery). Combined with mass spectrometry for protein identification, this TAP strategy facilitated the first nonbiased analysis of Btk interacting proteins. The high efficiency of the SBP-His₆ purification allows for efficient recovery of protein complexes formed with a target protein of interest from a small amount of starting material, enhancing the ability to detect low abundance and transient interactions in eukaryotic cell systems.
Figures


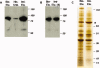
Similar articles
-
Protein-Protein Interaction: Tandem Affinity Purification in Bacteria.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1615:221-232. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7033-9_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28667616
-
Tandem affinity purification of protein complexes from mammalian cells by the Strep/FLAG (SF)-TAP tag.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;564:359-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-157-8_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19544034
-
Commonly used tag combinations for tandem affinity purification.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2010 Feb 15;55(2):73-83. doi: 10.1042/BA20090273. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20156193 Review.
-
Single-Step Affinity Purification of ERK Signaling Complexes Using the Streptavidin-Binding Peptide (SBP) Tag.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1487:113-126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6424-6_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27924562 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction proteomics: characterization of protein complexes using tandem affinity purification-mass spectrometry.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):883-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0380883. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20658971 Review.
Cited by
-
The structure of the SBP-Tag-streptavidin complex reveals a novel helical scaffold bridging binding pockets on separate subunits.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 May;69(Pt 5):879-87. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913002576. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23633599 Free PMC article.
-
Mutated in colorectal cancer (MCC) is a novel oncogene in B lymphocytes.J Hematol Oncol. 2014 Sep 9;7:56. doi: 10.1186/s13045-014-0056-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25200342 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling mechanisms of bortezomib in TRAF3-deficient mouse B lymphoma and human multiple myeloma cells.Leuk Res. 2016 Feb;41:85-95. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Leuk Res. 2016. PMID: 26740054 Free PMC article.
-
Native and tagged CENP-A histones are functionally inequivalent.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024 Jun 2;17(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13072-024-00543-9. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024. PMID: 38825690 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Fission Factor Is a Novel Interacting Protein of the Critical B Cell Survival Regulator TRAF3 in B Lymphocytes.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 20;12:670338. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.670338. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34745083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Puig O, Caspary F, Rigaut G, Rutz B, Bouveret E, Bragado-Nilsson E, Wilm M, Seraphin B. The tandem affinity purification (TAP) method: a general procedure of protein complex purification. Methods. 2001;24:218–229. - PubMed
-
- Rigaut G, Shevchenko A, Rutz B, Wilm M, Mann M, Seraphin B. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17:1030–1032. - PubMed
-
- Cox DM, Du M, Guo X, Siu KW, McDermott JC. Tandem affinity purification of protein complexes from mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 2002;33:267–268. 270. - PubMed
-
- Forler D, Kocher T, Rode M, Gentzel M, Izaurralde E, Wilm M. An efficient protein complex purification method for functional proteomics in higher eukaryotes. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:89–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

