A sequence-dependent exonuclease activity from Tetrahymena thermophila
- PMID: 21080963
- PMCID: PMC2998447
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-11-45
A sequence-dependent exonuclease activity from Tetrahymena thermophila
Abstract
Background: Telomere function requires a highly conserved G rich 3'- overhang. This structure is formed by 5'-resection of the C-rich telomere strand. However, while many nucleases have been suggested to play a role in processing, it is not yet clear which nucleases carry out this 5'-resection.
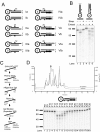
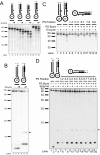
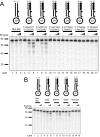
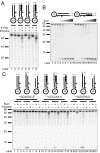
Results: We used biochemical purification to identify a sequence-dependent exonuclease activity in Tetrahymena thermophila cell extracts. The nuclease activity showed specificity for 5'-ends containing AA or AC sequences, unlike Exo1, which showed sequence-independent cleavage. The Tetrahymena nuclease was active on both phosphorylated and unphosphorylated substrates whereas Exo1 requires a 5'-phosphate for cleavage.
Conclusions: The specificities of the enzyme indicate that this novel Tetrahymena exonuclease is distinct from Exo1 and has properties required for 3'-overhang formations at telomeres.
Figures

References
-
- Harley CB. In: Methods in Mol Biol. Pollard JW, Walker JM, editor. Vol. 5. Clifton, NJ:The Humana Press Inc.; 1990. Aging in cultured human fibroblasts; pp. 25–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

