Discovery of entry inhibitors for HIV-1 via a new de novo protein design framework
- PMID: 21081094
- PMCID: PMC2980751
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.09.050
Discovery of entry inhibitors for HIV-1 via a new de novo protein design framework
Abstract
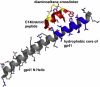
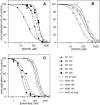
A new (to our knowledge) de novo design framework with a ranking metric based on approximate binding affinity calculations is introduced and applied to the discovery of what we believe are novel HIV-1 entry inhibitors. The framework consists of two stages: a sequence selection stage and a validation stage. The sequence selection stage produces a rank-ordered list of amino-acid sequences by solving an integer programming sequence selection model. The validation stage consists of fold specificity and approximate binding affinity calculations. The designed peptidic inhibitors are 12-amino-acids-long and target the hydrophobic core of gp41. A number of the best-predicted sequences were synthesized and their inhibition of HIV-1 was tested in cell culture. All peptides examined showed inhibitory activity when compared with no drug present, and the novel peptide sequences outperformed the native template sequence used for the design. The best sequence showed micromolar inhibition, which is a 3-15-fold improvement over the native sequence, depending on the donor. In addition, the best sequence equally inhibited wild-type and Enfuvirtide-resistant virus strains.
Copyright © 2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Creating an Artificial Tail Anchor as a Novel Strategy To Enhance the Potency of Peptide-Based HIV Fusion Inhibitors.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01445-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01445-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795416 Free PMC article.
-
The C4 region as a target for HIV entry inhibitors--NMR mapping of the interacting segments of T20 and gp120.FEBS J. 2015 Dec;282(24):4643-57. doi: 10.1111/febs.13541. Epub 2015 Oct 22. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 26432362 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of HIV-1 inhibitory peptide T20 with the gp41 N-HR coiled coil.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 6;284(6):3619-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809269200. Epub 2008 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19073602 Free PMC article.
-
Updating the use of synthetic peptides as inhibitors of HIV-1 entry.Curr Med Chem. 2014 Apr;21(10):1188-200. doi: 10.2174/15672050113109990204. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 23931277 Review.
-
HIV-1 gp41 heptad repeat 2 (HR2) possesses an amino acid domain that resembles the allergen domain in Aspergillus fumigatus Asp f1 protein: review, hypothesis and implications.Virus Genes. 2007 Jun;34(3):233-40. doi: 10.1007/s11262-007-0082-3. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Virus Genes. 2007. PMID: 17333401 Review.
Cited by
-
Rigorous Computational and Experimental Investigations on MDM2/MDMX-Targeted Linear and Macrocyclic Peptides.Molecules. 2019 Dec 14;24(24):4586. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244586. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31847417 Free PMC article.
-
Protein WISDOM: a workbench for in silico de novo design of biomolecules.J Vis Exp. 2013 Jul 25;(77):50476. doi: 10.3791/50476. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23912941 Free PMC article.
-
Derivation of ligands for the complement C3a receptor from the C-terminus of C5a.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec 15;745:176-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.10.041. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25446428 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating a key component of cancer metastasis: CXCL12 (SDF-1α) binding to CXCR4.J Chem Inf Model. 2014 Apr 28;54(4):1174-88. doi: 10.1021/ci500069y. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Chem Inf Model. 2014. PMID: 24660779 Free PMC article.
-
Computational methods for de novo protein design and its applications to the human immunodeficiency virus 1, purine nucleoside phosphorylase, ubiquitin specific protease 7, and histone demethylases.Curr Drug Targets. 2010 Mar;11(3):264-78. doi: 10.2174/138945010790711914. Curr Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20210752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- UNAIDS. 2008. 2008 Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic. XVII International AIDS Conference, International AIDS Society, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Thayer A.M. Resetting priorities. Chem. Eng. News. 2008;86:17–28.
-
- Thayer A.M. New antiretrovirals. Chem. Eng. News. 2008;86:29–36.
-
- Chan D.C., Kim P.S. HIV entry and its inhibition. Cell. 1998;93:681–684. - PubMed
-
- Liu S.W., Wu S.G., Jiang S.B. HIV entry inhibitors targeting gp41: from polypeptides to small-molecule compounds. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007;13:143–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

