Phosphorylation of phosphatidate phosphatase regulates its membrane association and physiological functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: identification of SER(602), THR(723), AND SER(744) as the sites phosphorylated by CDC28 (CDK1)-encoded cyclin-dependent kinase
- PMID: 21081492
- PMCID: PMC3020757
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.155598
Phosphorylation of phosphatidate phosphatase regulates its membrane association and physiological functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: identification of SER(602), THR(723), AND SER(744) as the sites phosphorylated by CDC28 (CDK1)-encoded cyclin-dependent kinase
Abstract
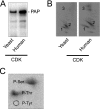
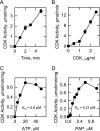
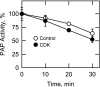
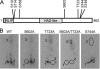
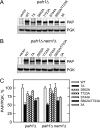
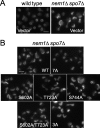
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae PAH1-encoded phosphatidate phosphatase (PAP) catalyzes the penultimate step in the synthesis of triacylglycerol and plays a role in the transcriptional regulation of phospholipid synthesis genes. PAP is phosphorylated at multiple Ser and Thr residues and is dephosphorylated for in vivo function by the Nem1p-Spo7p protein phosphatase complex localized in the nuclear/endoplasmic reticulum membrane. In this work, we characterized seven previously identified phosphorylation sites of PAP that are within the Ser/Thr-Pro motif. When expressed on a low copy plasmid, wild type PAP could not complement the pah1Δ mutant in the absence of the Nem1p-Spo7p complex. However, phosphorylation-deficient PAP (PAP-7A) containing alanine substitutions for the seven phosphorylation sites bypassed the requirement of the phosphatase complex and complemented the pah1Δ nem1Δ mutant phenotypes, such as temperature sensitivity, nuclear/endoplasmic reticulum membrane expansion, decreased triacylglycerol synthesis, and derepression of INO1 expression. Subcellular fractionation coupled with immunoblot analysis showed that PAP-7A was highly enriched in the membrane fraction. In fluorescence spectroscopy analysis, the PAP-7A showed tighter association with phospholipid vesicles than wild type PAP. Using site-directed mutagenesis of PAP, we identified Ser(602), Thr(723), and Ser(744), which belong to the seven phosphorylation sites, as the sites phosphorylated by the CDC28 (CDK1)-encoded cyclin-dependent kinase. Compared with the dephosphorylation mimic of the seven phosphorylation sites, alanine substitution for Ser(602), Thr(723), and/or Ser(744) had a partial effect on circumventing the requirement for the Nem1p-Spo7p complex.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

