Extensive role of the general regulatory factors, Abf1 and Rap1, in determining genome-wide chromatin structure in budding yeast
- PMID: 21081559
- PMCID: PMC3064788
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1161
Extensive role of the general regulatory factors, Abf1 and Rap1, in determining genome-wide chromatin structure in budding yeast
Abstract
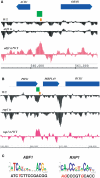
The packaging of eukaryotic DNA into chromatin has profound consequences for gene regulation, as well as for other DNA transactions such as recombination, replication and repair. Understanding how this packaging is determined is consequently a pressing problem in molecular genetics. DNA sequence, chromatin remodelers and transcription factors affect chromatin structure, but the scope of these influences on genome-wide nucleosome occupancy patterns remains uncertain. Here, we use high resolution tiling arrays to examine the contributions of two general regulatory factors, Abf1 and Rap1, to nucleosome occupancy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. These factors have each been shown to bind to a few hundred promoters, but we find here that thousands of loci show localized regions of altered nucleosome occupancy within 1 h of loss of Abf1 or Rap1 binding, and that altered chromatin structure can occur via binding sites having a wide range of affinities. These results indicate that DNA-binding transcription factors affect chromatin structure, and probably dynamics, throughout the genome to a much greater extent than previously appreciated.
Figures




References
-
- Owen-Hughes T, Workman JL. Experimental analysis of chromatin function in transcription control. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 1994;4:403–441. - PubMed
-
- Simpson RT. Nucleosome positioning: occurrence, mechanisms, and functional consequences. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1991;40:143–184. - PubMed
-
- Thoma F. Nucleosome positioning. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1992;1130:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Hirschhorn JN, Brown SA, Clark CD, Winston F. Evidence that SNF2/SWI2 and SNF5 activate transcription in yeast by altering chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1992;6:2288–2298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

