Image quality of multiplanar reconstruction of pulmonary CT scans using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction
- PMID: 21081572
- PMCID: PMC3473477
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/57998586
Image quality of multiplanar reconstruction of pulmonary CT scans using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction
Abstract
Objective: We investigated the image quality of multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR).
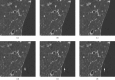
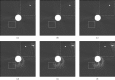
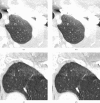
Methods: Inflated and fixed lungs were scanned with a garnet detector CT in high-resolution mode (HR mode) or non-high-resolution (HR) mode, and MPR images were then reconstructed. Observers compared 15 MPR images of ASIR (40%) and ASIR (80%) with those of ASIR (0%), and assessed image quality using a visual five-point scale (1, definitely inferior; 5, definitely superior), with particular emphasis on normal pulmonary structures, artefacts, noise and overall image quality.
Results: The mean overall image quality scores in HR mode were 3.67 with ASIR (40%) and 4.97 with ASIR (80%). Those in non-HR mode were 3.27 with ASIR (40%) and 3.90 with ASIR (80%). The mean artefact scores in HR mode were 3.13 with ASIR (40%) and 3.63 with ASIR (80%), but those in non-HR mode were 2.87 with ASIR (40%) and 2.53 with ASIR (80%). The mean scores of the other parameters were greater than 3, whereas those in HR mode were higher than those in non-HR mode. There were significant differences between ASIR (40%) and ASIR (80%) in overall image quality (p<0.01). Contrast medium in the injection syringe was scanned to analyse image quality; ASIR did not suppress the severe artefacts of contrast medium.
Conclusion: In general, MPR image quality with ASIR (80%) was superior to that with ASIR (40%). However, there was an increased incidence of artefacts by ASIR when CT images were obtained in non-HR mode.
Figures

References
-
- Arakawa H, Sasaka K, Lu WM, Hirayanagi N, Nakajima Y. Comparison of axial high-resolution CT and thin-section multiplanar reformation (MPR) for diagnosis of diseases of the pulmonary parenchyma: preliminary study in 49 patients. J Thorac Imaging 2004;19:24–31 - PubMed
-
- Choi EJ, Oh YW, Ham SY, Lee KY, Kang EY. Comparison between coronal reformatted images and direct coronal CT images of the swine lung specimen: assessment of image quality with 64-detector row CT. Br J Radiol 2008;81:463–7 - PubMed
-
- Pretorius PH, King MA, Pan TS, de Vries DJ, Glick SJ, Byrne CL. Reducing the influence of the partial volume effect on SPECT activity quantitation with 3D modelling of spatial resolution in iterative reconstruction. Phys Med Biol 1998;43:407–20 - PubMed
-
- Wells RG, King MA, Simkin PH, Judy PF, Brill AB, Gifford HC, et al. Comparing filtered backprojection and ordered-subsets expectation maximization for small-lesion detection and localization in 67Ga SPECT. J Nucl Med 2000;41:1391–9 - PubMed
-
- Knesaurek K, Machac J, Vallabhajosula S, Buchsbaum MS. A new iterative reconstruction technique for attenuation correction in high-resolution positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 1996;23:656–61 - PubMed

