Pazopanib reveals a role for tumor cell B-Raf in the prevention of HER2+ breast cancer brain metastasis
- PMID: 21081656
- PMCID: PMC3059742
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1603
Pazopanib reveals a role for tumor cell B-Raf in the prevention of HER2+ breast cancer brain metastasis
Abstract
Purpose: Brain metastases of breast cancer contribute significantly to patient morbidity and mortality. We have tested pazopanib, a recently approved antiangiogenic drug that targets VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFRβ, PDGFRα, and c-kit, for prevention of experimental brain metastases and mechanism of action.
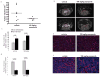
Experimental design: In vitro assays included B-Raf enzymatic assays, Western blots, and angiogenesis assays. For in vivo assays, HER2 transfectants of the brain seeking sublines of MDA-MB-231 cells (231-BR-HER2) and MCF7 cells (MCF7-HER2-BR3, derived herein) were injected into the left cardiac ventricle of mice and treated with vehicle or pazopanib beginning on day 3 postinjection. Brain metastases were counted histologically, imaged, and immunostained.
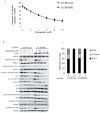
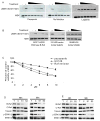
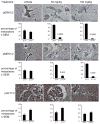
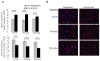
Results: Treatment with 100 mg/kg of pazopanib resulted in a 73% decline in large 231-BR-HER2 metastases (P < 0.0001) and a 39% decline in micrometastases (P = 0.004). In vitro, pazopanib was directly antiproliferative to 231-BR-HER2 breast cancer cells and inhibited MEK and ERK activation in vitro despite B-Raf and Ras mutations. Enzymatic assays demonstrated that pazopanib directly inhibited the wild type and exon 11 oncogenic mutant, but not the V600E mutant forms of B-Raf. Activation of the B-Raf targets pERK1/2 and pMEK1/2 was decreased in pazopanib-treated brain metastases whereas blood vessel density was unaltered. In the MCF7-HER2-BR3 experimental brain metastasis model, pazopanib reduced overall brain metastasis volume upon magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by 55% (P = 0.067), without affecting brain metastasis vascular density.
Conclusions: The data identify a new activity for pazopanib directly on tumor cells as a pan-Raf inhibitor and suggest its potential for prevention of brain metastatic colonization of HER2(+) breast cancer.
©2010 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Hicks D, Short S, Prescott N, Tarr S, Coleman K, Yoder B, et al. Breast cancers with brain metastases are more likely to be estrogen receptor negative, express the basal cytokeratin CK5/6 and over-express Her-2 or EGFR. Am J Surg Path. 2006;30:1097–104. - PubMed
-
- Bendell J, Domchek S, Burstein H, Harris L, Younger J, Kuter I, et al. Central Nervous System Metastases in Women who Receive Trastuzumab-Based Therapy for Metastatic Breast Carcinoma. Cancer. 2003;97:2972–7. - PubMed
-
- Stemmler HJ, Heinemann V. Central nervous system metastases in HER-2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer: a treatment challenge. Oncologist. 2008;13:739–50. - PubMed
-
- Kallioniemi OP, Holli K, Visakorpi T, Koivula T, Helin HH, Isola JJ. Association of c-erbB-2 protein over-expression with high rate of cell proliferation, increased risk of visceral metastasis and poor long-term survival in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1991;49:650–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

