Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor sitagliptin reduces local inflammation in adipose tissue and in pancreatic islets of obese mice
- PMID: 21081706
- PMCID: PMC3043624
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00463.2010
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor sitagliptin reduces local inflammation in adipose tissue and in pancreatic islets of obese mice
Abstract
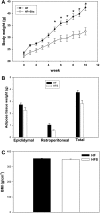
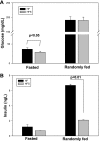
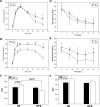
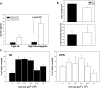
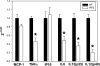
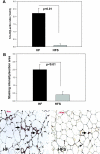
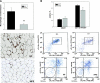
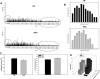
Adipose tissue inflammation and reduced pancreatic β-cell function are key issues in the development of cardiovascular disease and progressive metabolic dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of the DPP IV inhibitor sitagliptin on adipose tissue and pancreatic islet inflammation in a diet-induced obesity model. C57Bl/6J mice were placed on a high-fat (60% kcal fat) diet for 12 wk, with or without sitagliptin (4 g/kg) as a food admix. Sitagliptin significantly reduced fasting blood glucose by 21% as well as insulin by ∼25%. Sitagliptin treatment reduced body weight without changes in overall body mass index or in the epididymal and retroperitoneal fat mass. However, sitagliptin treatment led to triple the number of small adipocytes despite reducing the number of the very large adipocytes. Sitagliptin significantly reduced inflammation in the adipose tissue and pancreatic islet. Macrophage infiltration in adipose tissue evaluated by immunostaining for Mac2 was reduced by sitagliptin (P < 0.01), as was the percentage of CD11b+/F4/80+ cells in the stromal vascular fraction (P < 0.02). Sitagliptin also reduced adipocyte mRNA expression of inflammatory genes, including IL-6, TNFα, IL-12(p35), and IL-12(p40), 2.5- to fivefold as well as 12-lipoxygenase protein expression. Pancreatic islets were isolated from animals after treatments. Sitagliptin significantly reduced mRNA expression of the following inflammatory cytokines: MCP-1 (3.3-fold), IL-6 (2-fold), IL-12(p40) (2.2-fold), IL-12(p35) (5-fold, P < 0.01), and IP-10 (2-fold). Collectively, the results indicate that sitagliptin has anti-inflammatory effects in adipose tissue and in pancreatic islets that accompany the insulinotropic effect.
Figures

References
-
- Aaboe K, Knop FK, Vilsboll T, Deacon CF, Holst JJ, Madsbad S, Krarup T. Twelve weeks treatment with the DPP-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, prevents degradation of peptide YY and improves glucose and non-glucose induced insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab 12: 323–333, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Ahren B. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: clinical data and clinical implications. Diabetes Care 30: 1344–1350, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Ahren B, Holst JJ, Martensson H, Balkan B. Improved glucose tolerance and insulin secretion by inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 404: 239–245, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Allen TL, Febbraio MA. IL6 as a mediator of insulin resistance: fat or fiction? Diabetologia 53: 399–402, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Andersson CX, Gustafson B, Hammarstedt A, Hedjazifar S, Smith U. Inflamed adipose tissue, insulin resistance and vascular injury. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 24: 595–603, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

