Characterization of Nyquist ghost in EPI-fMRI acquisition sequences implemented on two clinical 1.5 T MR scanner systems: effect of readout bandwidth and echo spacing
- PMID: 21081879
- PMCID: PMC5720418
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v11i4.3237
Characterization of Nyquist ghost in EPI-fMRI acquisition sequences implemented on two clinical 1.5 T MR scanner systems: effect of readout bandwidth and echo spacing
Abstract
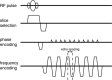
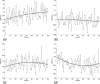
In EPI-fMRI acquisitions, various readout bandwidth (BW) values are used as a function of gradients' characteristics of the MR scanner system. Echo spacing (ES) is another fundamental parameter of EPI-fMRI sequences, but the employed ES value is not usually reported in fMRI studies. Nyquist ghost is a typical EPI artifact that can degrade the overall quality of fMRI time series. In this work, the authors assessed the basic effect of BW and ES for two clinical 1.5 T MR scanner systems (scanner-A, scanner-B) on Nyquist ghost of gradient-echo EPI-fMRI sequences. BW range was: scanner-A, 1953-3906 Hz/pixel; scanner-B, 1220-2894 Hz/pixel. ES range was: scanner-A, scanner-B: 0.75-1.33 ms. The ghost-to-signal ratio of time series acquisition (GSRts) and drift of ghost-to-signal ratio (DRGSR) were measured in a water phantom. For both scanner-A (93% of variation) and scanner-B (102% of variation) the mean GSRts significantly increased with increasing BW. GSRts values of scanner-A did not significantly depended on ES. On the other hand, GSRts values of scanner-B significantly varied with ES, showing a downward trend (81% of variation) with increasing ES. In addition, a GSRts spike point at ES = 1.05 ms indicating a potential resonant effect was revealed. For both scanners, no significant effect of ES on DRGSR was revealed. DRGSR values of scanner-B did not significantly vary with BW, whereas DRGSR values of scanner-A significantly depended on BW showing an upward trend from negative to positive values with increasing BW. GSRts and DRGSR can significantly vary with BW and ES, and the specific pattern of variation may depend on gradients performances, EPI sequence calibrations and functional design of radiofrequency coil. Thus, each MR scanner system should be separately characterized. In general, the employment of low BW values seems to reduce the intensity and temporal variation of Nyquist ghost in EPI-fMRI time series. On the other hand, the use of minimum ES value might not be entirely advantageous when the MR scanner is characterized by gradients with low performances and suboptimal EPI sequence calibration.
Figures



References
-
- Price RR, Allison J, Massoth RJ, Clarke JD, Drost DJ. Practical aspects of functional MRI (NMR Task Group #8). Med Phys. 2002;29(8):1892–912. - PubMed
-
- Matthews PM, Honey GD, Bullmore ET. Applications of fMRI in translational medicine and clinical practice. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(9):732–44. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa S, Menon RS, Kim SG, Ugurbil K. On the characteristics of functional magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998;27:447–74. - PubMed
-
- Logothetis NK. What we can do and what we cannot do with fMRI. Nature. 2008;453(7197):869–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

