Smaug assembles an ATP-dependent stable complex repressing nanos mRNA translation at multiple levels
- PMID: 21081899
- PMCID: PMC3020108
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.283
Smaug assembles an ATP-dependent stable complex repressing nanos mRNA translation at multiple levels
Abstract
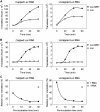
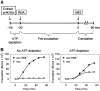
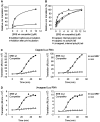
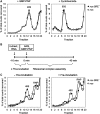
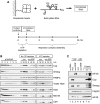
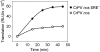
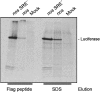
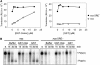
The nanos (nos) mRNA encodes the posterior determinant of the Drosophila embryo. Translation of the RNA is repressed throughout most of the embryo by the protein Smaug binding to Smaug recognition elements (SREs) in the 3' UTR. Translation is locally activated at the posterior pole by Oskar. This paper reports that the SREs govern the time- and ATP-dependent assembly of an exceedingly stable repressed ribonucleoprotein particle (RNP) in embryo extract. Repression can be virtually complete. Smaug and its co-repressor Cup as well as Trailer hitch and the DEAD box protein Me31B are part of the repressed RNP. The initiation factor eIF4G is specifically displaced, and 48S pre-initiation complex formation is inhibited. However, later steps in translation initiation are also sensitive to SRE-dependent inhibition. These data confirm several previously untested predictions of a current model for Cup-dependent repression but also suggest that the Cup model by itself is insufficient to explain translational repression of the nos RNA. In the embryo extract, recombinant Oskar relieves translational repression and deadenylation by preventing Smaug's binding to the SREs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aviv T, Lin Z, Ben-Ari G, Smibert CA, Sicheri F (2006) Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by the SAM domain of Vts1p. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13: 168–176 - PubMed
-
- Aviv T, Lin Z, Lau S, Rendl LM, Sicheri F, Smibert CA (2003) The RNA binding SAM domain of Smaug defines a new family of post-transcriptional regulators. Nat Struct Biol 10: 614–621 - PubMed
-
- Barbee SA, Estes PS, Cziko A-M, Hillebrand J, Luedeman RA, Coller JM, Johnson N, Howlett IC, Geng C, Ueda R, Brand AH, Newbury SF, Wilhelm JE, Levine RB, Nakamura A, Parker R, Ramaswami M (2006) Staufen- and FMRP-containing neuronal RNPs are structurally and functionally related to somatic P bodies. Neuron 52: 997–1009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bashirullah A, Halsell SR, Cooperstock RL, Kloc M, Karaiskakis A, Fisher WW, Fu W, Hamilton JK, Etkin LD, Lipshitz HD (1999) Joint action of two RNA degradation pathways controls the timing of maternal transcript elimination at the midblastula transition in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J 18: 2610–2620 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergsten SE, Gavis ER (1999) Role for mRNA localization in translational activation but not spatial restriction of nanos RNA. Development 126: 659–669 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

