mRNA turnover rate limits siRNA and microRNA efficacy
- PMID: 21081925
- PMCID: PMC3010119
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2010.89
mRNA turnover rate limits siRNA and microRNA efficacy
Abstract
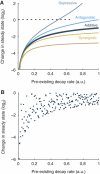
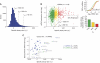
The microRNA pathway participates in basic cellular processes and its discovery has enabled the development of si/shRNAs as powerful investigational tools and potential therapeutics. Based on a simple kinetic model of the mRNA life cycle, we hypothesized that mRNAs with high turnover rates may be more resistant to RNAi-mediated silencing. The results of a simple reporter experiment strongly supported this hypothesis. We followed this with a genome-wide scale analysis of a rich corpus of experiments, including RT-qPCR validation data for thousands of siRNAs, siRNA/microRNA overexpression data and mRNA stability data. We find that short-lived transcripts are less affected by microRNA overexpression, suggesting that microRNA target prediction would be improved if mRNA turnover rates were considered. Similarly, short-lived transcripts are more difficult to silence using siRNAs, and our results may explain why certain transcripts are inherently recalcitrant to perturbation by small RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
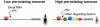
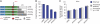
References
-
- Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T (2001) Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 411: 494–498 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

