Utility of biodegradable plasmonic nanoclusters in photoacoustic imaging
- PMID: 21081985
- PMCID: PMC3071708
- DOI: 10.1364/OL.35.003751
Utility of biodegradable plasmonic nanoclusters in photoacoustic imaging
Abstract
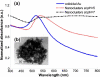
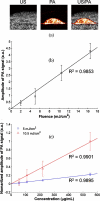
Plasmonic metal nanoparticles are used in photoacoustic imaging as contrast agents because of their resonant optical absorption properties in the visible and near-IR regions. However, the nanoparticles could accumulate and result in long-term toxicity in vivo, because they are generally not biodegradable. Recently, biodegradable plasmonic gold nanoclusters, consisting of sub-5 nm primary gold nanoparticles and biodegradable polymer stabilizer, were introduced. In this Letter, we demonstrate the feasibility of biodegradable nanoclusters as a photoacoustic contrast agent. We performed photoacoustic and ultrasound imaging of a tissue-mimicking phantom with inclusions containing nanoclusters at various concentrations. The results indicate that the biodegradable gold nanoclusters can be used as effective contrast agents in photoacoustic imaging.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

