A draft of the human septin interactome
- PMID: 21082023
- PMCID: PMC2970546
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013799
A draft of the human septin interactome
Abstract
Background: Septins belong to the GTPase superclass of proteins and have been functionally implicated in cytokinesis and the maintenance of cellular morphology. They are found in all eukaryotes, except in plants. In mammals, 14 septins have been described that can be divided into four groups. It has been shown that mammalian septins can engage in homo- and heterooligomeric assemblies, in the form of filaments, which have as a basic unit a hetero-trimeric core. In addition, it has been speculated that the septin filaments may serve as scaffolds for the recruitment of additional proteins.
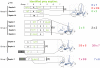
Methodology/principal findings: Here, we performed yeast two-hybrid screens with human septins 1-10, which include representatives of all four septin groups. Among the interactors detected, we found predominantly other septins, confirming the tendency of septins to engage in the formation of homo- and heteropolymeric filaments.
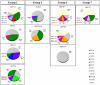
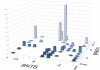
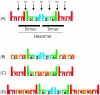
Conclusions/significance: If we take as reference the reported arrangement of the septins 2, 6 and 7 within the heterofilament, (7-6-2-2-6-7), we note that the majority of the observed interactions respect the "group rule", i.e. members of the same group (e.g. 6, 8, 10 and 11) can replace each other in the specific position along the heterofilament. Septins of the SEPT6 group preferentially interacted with septins of the SEPT2 group (p<0.001), SEPT3 group (p<0.001) and SEPT7 group (p<0.001). SEPT2 type septins preferentially interacted with septins of the SEPT6 group (p<0.001) aside from being the only septin group which interacted with members of its own group. Finally, septins of the SEPT3 group interacted preferentially with septins of the SEPT7 group (p<0.001). Furthermore, we found non-septin interactors which can be functionally attributed to a variety of different cellular activities, including: ubiquitin/sumoylation cycles, microtubular transport and motor activities, cell division and the cell cycle, cell motility, protein phosphorylation/signaling, endocytosis, and apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
SUMOylation of human septins is critical for septin filament bundling and cytokinesis.J Cell Biol. 2017 Dec 4;216(12):4041-4052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201703096. Epub 2017 Oct 19. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 29051266 Free PMC article.
-
Production and analysis of a mammalian septin hetero-octamer complex.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020 Nov;77(11):485-499. doi: 10.1002/cm.21643. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 33185030 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of human septin interactions.Biol Chem. 2011 Aug;392(8-9):751-61. doi: 10.1515/BC.2011.081. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21767235
-
The Mammalian Septin Interactome.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Feb 7;5:3. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00003. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28224124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding post-translational modifications of mammalian septins.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2023 Jul-Aug;80(7-8):169-181. doi: 10.1002/cm.21747. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 36797225 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial guidance of cell asymmetry: septin GTPases show the way.Traffic. 2012 Feb;13(2):195-203. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01268.x. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Traffic. 2012. PMID: 21883761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A requirement for septins and the autophagy receptor p62 in the proliferation of intracellular Shigella.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019 Jan;76(1):163-172. doi: 10.1002/cm.21453. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 29752866 Free PMC article.
-
The Ordospora colligata genome: Evolution of extreme reduction in microsporidia and host-to-parasite horizontal gene transfer.mBio. 2015 Jan 13;6(1):e02400-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02400-14. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25587016 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Disulfide Isomerase Modulates the Activation of Thyroid Hormone Receptors.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jan 8;9:784. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00784. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30671024 Free PMC article.
-
An Interaction Network of the Human SEPT9 Established by Quantitative Mass Spectrometry.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 Jun 5;9(6):1869-1880. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400197. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30975701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weirich CS, Erzberger JP, Barral Y. Nature Reviews, Molecular Cell Biology. 2008;9:478–489. - PubMed
-
- Peterson EA, Kalikin LM, Steels JD, Estey MP, Trimble WS, et al. Characterization of a SEPT9 interacting protein, SEPT14, a novel testis-specific septin. Mamm Genome. 2007;18:796–807. - PubMed
-
- McIlhatton MA, Burrows JF, Donaghy PG, Chanduloy S, Johnston PG, et al. Genomic organization, complex splicing pattern and expression of a human septin gene on chromosome 17q25.3. Oncogene. 2001;20:5930–5939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

