SIRT1 deficiency downregulates PTEN/JNK/FOXO1 pathway to block reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis in mouse embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 21083429
- PMCID: PMC3121936
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2010.0465
SIRT1 deficiency downregulates PTEN/JNK/FOXO1 pathway to block reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis in mouse embryonic stem cells
Abstract
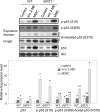
Silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 (SIRT1) plays a critical role in reactive oxygen species-triggered apoptosis in mouse embryonic stem (mES) cells. Here, we investigated a possible role for the PTEN/Akt/JNK pathway in the SIRT1-mediated apoptosis pathway in mES cells. Akt was activated by removal of anti-oxidant 2-mercaptoethanol in SIRT1(-/-) mES cells. Since PTEN is a negative regulator of Akt and its activity can be modulated by acetylation, we investigated if SIRT1 deacetylated PTEN to downregulate Akt to trigger apoptosis in anti-oxidant-free culture conditions. PTEN was hyperacetylated and excluded from the nucleus in SIRT1(-/-) mES cells, consistent with enhanced Akt activity. SIRT1 deficiency enhanced the acetylation/phosphorylation level of FOXO1 and subsequently inhibited the nuclear localization of FOXO1. Cellular acetylation levels were enhanced by DNA-damaging agent, not by removal of anti-oxidant. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) was activated by removal of anti-oxidant in SIRT1-dependent manner. Although p53 acetylation was stronger in SIRT1(-/-) mES cells, DNA-damaging stress activated phosphorylation and enhanced cellular levels of p53 irrespective of SIRT1, whereas removal of anti-oxidant slightly activated p53 only with SIRT1. Expression levels of Bim and Puma were increased in anti-oxidant-free culture conditions in an SIRT1-dependent manner and treatment with JNK inhibitor blocked induction of Bim expression. DNA-damaging agent activated caspase3 regardless of SIRT1. Our data support an important role for SIRT1 in preparing the PTEN/JNK/FOXO1 pathway to respond to cellular reactive oxygen species.
Figures
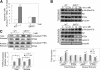
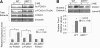



References
-
- Odorico JS. Kaufman DS. Thomson JA. Multilineage differentiation from human embryonic stem cell lines. Stem Cells. 2001;19:193–204. - PubMed
-
- Saretzki G. Armstrong L. Leake A. Lako M. von Zglinicki T. Stress defense in murine embryonic stem cells is superior to that of various differentiated murine cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22:962–971. - PubMed
-
- D'Autreaux B. Toledano MB. ROS as signalling molecules: mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:813–824. - PubMed
-
- Covarrubias L. Hernandez-Garcia D. Schnabel D. Salas-Vidal E. Castro-Obregon S. Function of reactive oxygen species during animal development: passive or active? Dev Biol. 2008;320:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

