Disruption of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-prolyl hydroxylase domain-1 (PHD-1-/-) attenuates ex vivo myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through hypoxia-inducible factor-1α transcription factor and its target genes in mice
- PMID: 21083501
- PMCID: PMC3159109
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3769
Disruption of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-prolyl hydroxylase domain-1 (PHD-1-/-) attenuates ex vivo myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through hypoxia-inducible factor-1α transcription factor and its target genes in mice
Abstract
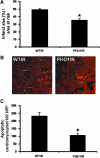
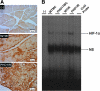
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (HIF)-prolyl hydroxylases domain (PHD-1-3) are oxygen sensors that regulate the stability of the HIFs in an oxygen-dependent manner. Suppression of PHD enzymes leads to stabilization of HIFs and offers a potential treatment option for many ischemic disorders, such as peripheral artery occlusive disease, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Here, we show that homozygous disruption of PHD-1 (PHD-1(-/-)) could facilitate HIF-1α-mediated cardioprotection in ischemia/reperfused (I/R) myocardium. Wild-type (WT) and PHD-1(-/-) mice were randomized into WT time-matched control (TMC), PHD-1(-/-) TMC (PHD1TMC), WT I/R, and PHD-1(-/-) I/R (PHD1IR). Isolated hearts from each group were subjected to 30 min of global ischemia followed by 2 h of reperfusion. TMC hearts were perfused for 2 h 30 min without ischemia. Decreased infarct size (35%±0.6% vs. 49%±0.4%) and apoptotic cardiomyocytes (106±13 vs. 233±21 counts/100 high-power field) were observed in PHD1IR compared to wild-type ischemia/reperfusion (WTIR). Protein expression of HIF-1α was significantly increased in PHD1IR compared to WTIR. mRNA expression of β-catenin (1.9-fold), endothelial nitric oxide synthase (1.9-fold), p65 (1.9-fold), and Bcl-2 (2.7-fold) were upregulated in the PHD1IR compared with WTIR, which was studied by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Further, gel-shift analysis showed increased DNA binding activity of HIF-1α and nuclear factor-kappaB in PHD1IR compared to WTIR. In addition, nuclear translocation of β-catenin was increased in PHD1IR compared with WTIR. These findings indicated that silencing of PHD-1 attenuates myocardial I/R injury probably by enhancing HIF-1α/β-catenin/endothelial nitric oxide synthase/nuclear factor-kappaB and Bcl-2 signaling pathway.
Figures

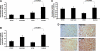

References
-
- Aragones J. Schneider M. Van Geyte K. Fraisl P. Dresselaers T. Mazzone M. Dirkx R. Zacchigna S. Lemieux H. Jeoung NH. Lambrechts D. Bishop T. Lafuste P. Diez-Juan A. Harten SK. Van Noten P. De Bock K. Willam C. Tjwa M. Grosfeld A. Navet R. Moons L. Vandendriessche T. Deroose C. Wijeyekoon B. Nuyts J. Jordan B. Silasi-Mansat R. Lupu F. Dewerchin M. Pugh C. Salmon P. Mortelmans L. Gallez B. Gorus F. Buyse J. Sluse F. Harris RA. Gnaiger E. Hespel P. Van Hecke P. Schuit F. Van Veldhoven P. Ratcliffe P. Baes M. Maxwell P. Carmeliet P. Deficiency or inhibition of oxygen sensor Phd1 induces hypoxia tolerance by reprogramming basal metabolism. Nat Genet. 2008;40:170–180. - PubMed
-
- Bao W. Qin P. Needle S. Erickson-Miller CL. Duffy KJ. Ariazi JL. Zhao S. Olzinski AR. Behm DJ. Pipes GC. Jucker BM. Hu E. Lepore JJ. Willette RN. Chronic inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl 4-hydroxylase improves ventricular performance, remodeling, and vascularity after myocardial infarction in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010;56:147–155. - PubMed
-
- Eckle T. Kohler D. Lehmann R. El Kasmi K. Eltzschig HK. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 is central to cardioprotection: a new paradigm for ischemic preconditioning. Circulation. 2008;118:166–175. - PubMed
-
- Foadoddini M. Esmailidehaj M. Mehrani H. Sadraei SH. Golmanesh L. Wahhabaghai H. Valen G. Khoshbaten A. Pretreatment with hyperoxia reduces in vivo infarct size and cell death by apoptosis with an early and delayed phase of protection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;39:233–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

