Morphologic, genetic, and biochemical characterization of Helicobacter magdeburgensis, a novel species isolated from the intestine of laboratory mice
- PMID: 21083746
- PMCID: PMC4369761
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2010.00770.x
Morphologic, genetic, and biochemical characterization of Helicobacter magdeburgensis, a novel species isolated from the intestine of laboratory mice
Abstract
Background: The presence of enterohepatic Helicobacter species (EHS) is commonly noted in mouse colonies. These infections often remain unrecognized but can cause severe health complications or more subtle host immune perturbations and therefore can confound the results of animal experiments. The aim of this study was to isolate and characterize a putative novel EHS that has previously been detected by PCR screening of specific-pathogen-free mice.
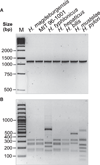
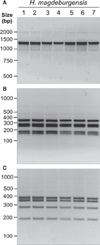
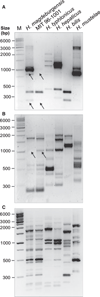
Materials and methods: Biochemical analysis of enzyme activities (API campy), morphologic investigation (Gram-staining and electron microscopy) and genetic analyses (16SrRNA and 23SrRNA analyses, DNA fingerprinting, restriction fragment polymorphisms, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis) were used to characterize isolated EHS. Genomic DNA fragments were sequenced to develop a species-specific PCR detection assay.
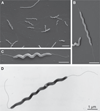
Results: Scanning electron microscopy revealed the presence of spiral-shaped EHS, which varied in length (2.5-6 μm) and contained single monopolar or single bipolar sheathed flagella. The bacteria were grown under anaerobic conditions, preferably on agar plates containing serum or blood. The 16SrRNA, genetic, and biochemical analyses indicated the identification of a novel EHS species, named Helicobacter magdeburgensis. We also examined the genome content using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Based on the pattern produced by two restriction enzymes, BamIII and KspI, the genome size was determined to be about 1.7-1.8 Mbp.
Conclusion: We isolated and characterized a novel EHS species, H. magdeburgensis, morphologically, biochemically, and genetically. These results are important for future studies on the prevalence and pathophysiologic relevance of such infections. Our PCR assay can be used to detect and discriminate H. magdeburgensis from other Helicobacter species.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Dewhirst FE, Fox JG, On SL. Recommended minimal standards for describing new species of the genus Helicobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000;50:2231–2237. - PubMed
-
- Marshall BJ, Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984;1:1311–1315. - PubMed
-
- Marshall BJ, Royce H, Annear DI, et al. Original isolation of Campylobacter pyloridis from human gastric mucosa. Microbios. 1984;25:83–88.
-
- Paster BJ, Dewhirst FE. Phylogeny of Campylobacter, wolinellas, Bacteroides gracilis, and Bacteroides ureolyticus by 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid sequencing. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1988;38:56–62.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

